搜索到
33
篇与
的结果
-
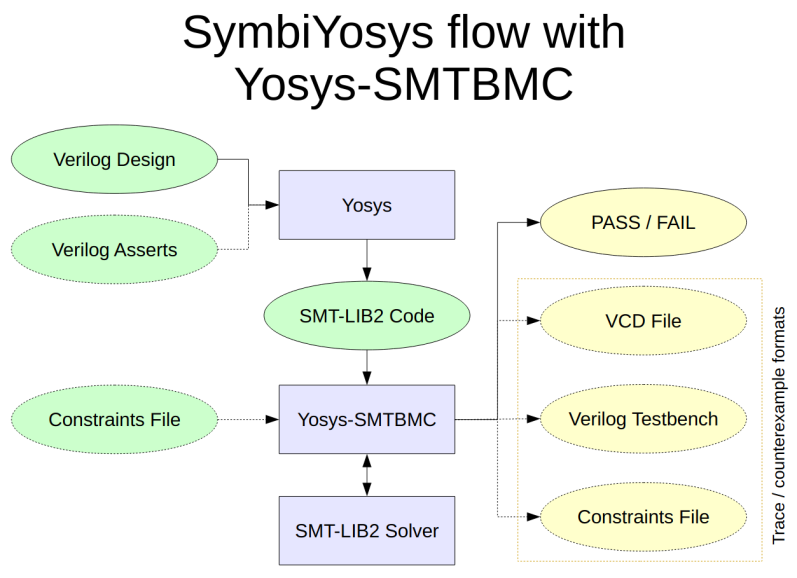
 使用 SymbiYosys 进行验证 Yosys 是一个开源的 Verilog HDL 综合工具包。它支持将电路的状态转换编码为 SMT-LIBv2 中的函数。由此出发,可以对电路进行一系列形式化验证。注意本文仅对相关工具的一般使用方法进行介绍,不涉及验证原理、算法分析等内容。本文讨论的内容均为 Assertion Based Verification (ABV),除此之外 Yosys 还支持 Symbolic Model Checking、Formal Equivalence Checking,相关用法有待进一步整理。Motivating Exampletest.v 定义了一个简单的时序逻辑电路(此示例电路来自 Yosys Command Reference Manual),它只有输出,没有输入。它的输出可以理解为一个数列 yn+1=or(shl(yn),neg(yn)),首项 y0 的值是电路的初始状态。module test(input clk, output reg [3:0] y); always @(posedge clk) y <= (y << 1) | ^y; endmodule我们的目标是验证输出 y 的值不可能从一个非零值变为一个零值。为了验证该性质,需要将其写为 SMT-LIBv2 表达式,交给 SMT solver 求解。因此,首先需要明白编码电路的方式。使用以下综合脚本(synthesis script)test.ys 指示 Yosys 对电路进行变换,得到 test.smt2 文件。# Read Verilog source file and convert to internal representation .read_verilog test.v # Elaborate the design hierarchy. # Should always be the first command after reading the design. hierarchy -check -top test # Convert “processes” (the internal representation of behavioral Verilog code) # into multiplexers and registers .proc # Perform some basic optimizations and cleanups .opt # Check for obvious problems in the design .check -assert # Write a SMT-LIBv2 description of the current design .write_smt2 test.smt2理解 synthesis script以上脚本包含了3种类型的指令:Frontends:从文件中读取输入(一般为 Verilog 代码)Passes:在电路上应用等价变换Backends:将处理后的电路输出到文件(支持不同的格式,如 Verilog, BLIF, EDIF, SPICE, BTOR 等)这也是所有典型的 Yosys synthesis script 都具有的结构,由此可见综合的过程与编译的过程非常相似。事实上,Yosys 定义了一种电路的中间表示格式 RTLIL (RTL Intermediate Language),所有的 Passes 都是在以此 IR 表示的抽象语法树(AST)上实现的。1 $ yosys test.ysYosys 输出的文件如下。此文件中定义了一个对应电路状态的类型 |_s|;电路中的输入(input)、输出(output)、寄存器(register)、线路(wire)都有各自对应的函数,这些函数名为 |_n |,它们接受一个电路状态作为输入,返回 Bool 类型或 BitVec 类型,对应具体的值。另外一个重要的函数为 |_t|,它接受两个状态 state, next_state 作为输入,当两者之间存在状态转换关系时,则返回 True,反之则返回 False。它们组合起来编码了电路的行为。SMT-LIBv2 description generated by Yosys 0.21+7 (git sha1 d98738db5, clang 10.0.0-4ubuntu1 -fPIC -Os); yosys-smt2-module test(declare-sort |test_s| 0)(declare-fun |test_is| (|test_s|) Bool)(declare-fun |test#0| (|test_s|) Bool) ; \clk; yosys-smt2-input clk 1; yosys-smt2-clock clk posedge; yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\clk"], "smtname": "clk", "type": "posedge", "width": 1}; yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\clk"], "smtname": "clk", "type": "input", "width": 1}(define-fun |test_n clk| ((state |test_s|)) Bool (|test#0| state)); yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\y"], "smtname": 1, "type": "reg", "width": 4}(declare-fun |test#1| (|test_s|) (_ BitVec 4)) ; \y; yosys-smt2-output y 4;yosys-smt2-register y 4(define-fun |test_n y| ((state |test_s|)) (_ BitVec 4) (|test#1| state))(define-fun |test#2| ((state |test_s|)) Bool (xor (= ((_ extract 0 0) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 1 1) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 2 2) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 3 3) (|test#1| state)) #b1))) ; $reduce_xor $test.v:3$3_Y(define-fun |test#3| ((state |test_s|)) (_ BitVec 4) (bvor (concat ((_ extract 2 0) (|test#1| state)) #b0) (concat #b000 (ite (|test#2| state) #b1 #b0)))) ; $0\y3:0) Bool true)(define-fun |test_u| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_i| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_h| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_t| ((state |test_s|) (next_state |test_s|)) Bool (= (|test#3| state) (|test#1| next_state)) ; $procdff$5 \y) ; end of module test; yosys-smt2-topmod test; end of yosys output现在,为了表示上述性质,可以定义两个状态 s1, s2,它们满足:1.s1 到 s2 存在状态转换关系2.s1 中 y != 03.s2 中 y == 0之后交给 SMT solver 验证其可满足性,若不能满足,则验证了不存在这样的情况。 we need QF_UFBV for this proof(set-logic QF_UFBV); insert the auto-generated code here%%; declare two state variables s1 and s2(declare-fun s1 () test_s)(declare-fun s2 () test_s); state s2 is the successor of state s1(assert (test_t s1 s2)); we are looking for a model with y non-zero in s1(assert (distinct (|test_n y| s1) #b0000)); we are looking for a model with y zero in s2(assert (= (|test_n y| s2) #b0000)); is there such a model?(check-sat)将上面的 test.ys 最后一行修改为:1 write_smt2 -tpl test.tpl test.smt2新的输出文件中包含了模版文件 test.tpl 的内容,并将其中的 %% 替换为了原本 write_smt2 命令的输出,可以将它作为 SMT solver 的输入。例如,调用 z3 进行求解,得到 unsat 的结果。12 $ z3 test.smt2unsat使用 SymbiYosys 进行验证上一节介绍的方法需要用户理解 write_smt2 命令的输出,并直接使用其中定义的函数,才能将需要验证的性质编写为 SMT-LIBv2 格式的表达式,这样不免有些繁琐。Yosys 还提供了 SymbiYosys (sby) 工具,它可以理解为一个前端驱动程序(front-end driver program),支持解析用户在源文件中定义的断言(assertions),直接尝试进行证明。来看另一个例子,下面是用 System Verilog 定义的一个计数器(此示例代码来自参考资料中 Formal Verification of RISC-V cores with riscv-formal 这一幻灯片的第3~4页)。module hello ( input clk, rst, output [3:0] cnt); reg [3:0] cnt = 0; always @(posedge clk) begin if (rst) cnt <= 0; else cnt <= cnt + 1; endendmodule现在来定义此电路需要满足的性质。首先用1个 assume 语句表明验证的前提(也就是在求解器考虑的所有情形中,此性质都得到满足);assert 语句则是求解器需要证明的性质。module hello (/* ... */);/* ... */ `ifdef FORMAL always @* assume (cnt != 10); always @* assert (cnt != 15); `endif endmoduleSymbiYosys 使用一个 .sby 文件来描述验证过程中执行的任务,文件中包含若干个节(section),每个节由方括号括起的小标题表示。下面的文件中,[options] 节将证明模式设置为“使用 Unbounded model check 验证 safety properties”,并且将 k-induction 的深度设置为10;[script] 中是处理输入文件用到的 Yosys 命令;输入文件列在 [files] 节中。关于 .sby 文件语法的更多信息请参考 Reference for .sby file format,这里并不展开说明。mode provedepth 10[engines] smtbmc z3[script] read_verilog -formal hello.sv prep -top hello[files] hello.sv将上面的两个文件放在同一目录下,然后调用 sby 程序,即可获得证明结果。$ sby -f hello.sby...SBY 19:06:39[hello] engine_0.induction: finished (returncode=0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] engine_0: Status returned by engine for induction: pass...SBY 19:06:39 [hello] engine_0.basecase: finished (returncode=0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] engine_0: Status returned by engine for basecase: passSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: Elapsed clock time [H:MM:SS (secs)]: 0:00:00 (0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: Elapsed process time [H:MM:SS (secs)]: 0:00:00 (0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: engine_0 (smtbmc z3) returned pass for inductionSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: engine_0 (smtbmc z3) returned pass for basecaseSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: successful proof by k-induction.SBY 19:06:39 [hello] DONE (PASS, rc=0)
使用 SymbiYosys 进行验证 Yosys 是一个开源的 Verilog HDL 综合工具包。它支持将电路的状态转换编码为 SMT-LIBv2 中的函数。由此出发,可以对电路进行一系列形式化验证。注意本文仅对相关工具的一般使用方法进行介绍,不涉及验证原理、算法分析等内容。本文讨论的内容均为 Assertion Based Verification (ABV),除此之外 Yosys 还支持 Symbolic Model Checking、Formal Equivalence Checking,相关用法有待进一步整理。Motivating Exampletest.v 定义了一个简单的时序逻辑电路(此示例电路来自 Yosys Command Reference Manual),它只有输出,没有输入。它的输出可以理解为一个数列 yn+1=or(shl(yn),neg(yn)),首项 y0 的值是电路的初始状态。module test(input clk, output reg [3:0] y); always @(posedge clk) y <= (y << 1) | ^y; endmodule我们的目标是验证输出 y 的值不可能从一个非零值变为一个零值。为了验证该性质,需要将其写为 SMT-LIBv2 表达式,交给 SMT solver 求解。因此,首先需要明白编码电路的方式。使用以下综合脚本(synthesis script)test.ys 指示 Yosys 对电路进行变换,得到 test.smt2 文件。# Read Verilog source file and convert to internal representation .read_verilog test.v # Elaborate the design hierarchy. # Should always be the first command after reading the design. hierarchy -check -top test # Convert “processes” (the internal representation of behavioral Verilog code) # into multiplexers and registers .proc # Perform some basic optimizations and cleanups .opt # Check for obvious problems in the design .check -assert # Write a SMT-LIBv2 description of the current design .write_smt2 test.smt2理解 synthesis script以上脚本包含了3种类型的指令:Frontends:从文件中读取输入(一般为 Verilog 代码)Passes:在电路上应用等价变换Backends:将处理后的电路输出到文件(支持不同的格式,如 Verilog, BLIF, EDIF, SPICE, BTOR 等)这也是所有典型的 Yosys synthesis script 都具有的结构,由此可见综合的过程与编译的过程非常相似。事实上,Yosys 定义了一种电路的中间表示格式 RTLIL (RTL Intermediate Language),所有的 Passes 都是在以此 IR 表示的抽象语法树(AST)上实现的。1 $ yosys test.ysYosys 输出的文件如下。此文件中定义了一个对应电路状态的类型 |_s|;电路中的输入(input)、输出(output)、寄存器(register)、线路(wire)都有各自对应的函数,这些函数名为 |_n |,它们接受一个电路状态作为输入,返回 Bool 类型或 BitVec 类型,对应具体的值。另外一个重要的函数为 |_t|,它接受两个状态 state, next_state 作为输入,当两者之间存在状态转换关系时,则返回 True,反之则返回 False。它们组合起来编码了电路的行为。SMT-LIBv2 description generated by Yosys 0.21+7 (git sha1 d98738db5, clang 10.0.0-4ubuntu1 -fPIC -Os); yosys-smt2-module test(declare-sort |test_s| 0)(declare-fun |test_is| (|test_s|) Bool)(declare-fun |test#0| (|test_s|) Bool) ; \clk; yosys-smt2-input clk 1; yosys-smt2-clock clk posedge; yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\clk"], "smtname": "clk", "type": "posedge", "width": 1}; yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\clk"], "smtname": "clk", "type": "input", "width": 1}(define-fun |test_n clk| ((state |test_s|)) Bool (|test#0| state)); yosys-smt2-witness {"offset": 0, "path": ["\y"], "smtname": 1, "type": "reg", "width": 4}(declare-fun |test#1| (|test_s|) (_ BitVec 4)) ; \y; yosys-smt2-output y 4;yosys-smt2-register y 4(define-fun |test_n y| ((state |test_s|)) (_ BitVec 4) (|test#1| state))(define-fun |test#2| ((state |test_s|)) Bool (xor (= ((_ extract 0 0) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 1 1) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 2 2) (|test#1| state)) #b1) (= ((_ extract 3 3) (|test#1| state)) #b1))) ; $reduce_xor $test.v:3$3_Y(define-fun |test#3| ((state |test_s|)) (_ BitVec 4) (bvor (concat ((_ extract 2 0) (|test#1| state)) #b0) (concat #b000 (ite (|test#2| state) #b1 #b0)))) ; $0\y3:0) Bool true)(define-fun |test_u| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_i| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_h| ((state |test_s|)) Bool true)(define-fun |test_t| ((state |test_s|) (next_state |test_s|)) Bool (= (|test#3| state) (|test#1| next_state)) ; $procdff$5 \y) ; end of module test; yosys-smt2-topmod test; end of yosys output现在,为了表示上述性质,可以定义两个状态 s1, s2,它们满足:1.s1 到 s2 存在状态转换关系2.s1 中 y != 03.s2 中 y == 0之后交给 SMT solver 验证其可满足性,若不能满足,则验证了不存在这样的情况。 we need QF_UFBV for this proof(set-logic QF_UFBV); insert the auto-generated code here%%; declare two state variables s1 and s2(declare-fun s1 () test_s)(declare-fun s2 () test_s); state s2 is the successor of state s1(assert (test_t s1 s2)); we are looking for a model with y non-zero in s1(assert (distinct (|test_n y| s1) #b0000)); we are looking for a model with y zero in s2(assert (= (|test_n y| s2) #b0000)); is there such a model?(check-sat)将上面的 test.ys 最后一行修改为:1 write_smt2 -tpl test.tpl test.smt2新的输出文件中包含了模版文件 test.tpl 的内容,并将其中的 %% 替换为了原本 write_smt2 命令的输出,可以将它作为 SMT solver 的输入。例如,调用 z3 进行求解,得到 unsat 的结果。12 $ z3 test.smt2unsat使用 SymbiYosys 进行验证上一节介绍的方法需要用户理解 write_smt2 命令的输出,并直接使用其中定义的函数,才能将需要验证的性质编写为 SMT-LIBv2 格式的表达式,这样不免有些繁琐。Yosys 还提供了 SymbiYosys (sby) 工具,它可以理解为一个前端驱动程序(front-end driver program),支持解析用户在源文件中定义的断言(assertions),直接尝试进行证明。来看另一个例子,下面是用 System Verilog 定义的一个计数器(此示例代码来自参考资料中 Formal Verification of RISC-V cores with riscv-formal 这一幻灯片的第3~4页)。module hello ( input clk, rst, output [3:0] cnt); reg [3:0] cnt = 0; always @(posedge clk) begin if (rst) cnt <= 0; else cnt <= cnt + 1; endendmodule现在来定义此电路需要满足的性质。首先用1个 assume 语句表明验证的前提(也就是在求解器考虑的所有情形中,此性质都得到满足);assert 语句则是求解器需要证明的性质。module hello (/* ... */);/* ... */ `ifdef FORMAL always @* assume (cnt != 10); always @* assert (cnt != 15); `endif endmoduleSymbiYosys 使用一个 .sby 文件来描述验证过程中执行的任务,文件中包含若干个节(section),每个节由方括号括起的小标题表示。下面的文件中,[options] 节将证明模式设置为“使用 Unbounded model check 验证 safety properties”,并且将 k-induction 的深度设置为10;[script] 中是处理输入文件用到的 Yosys 命令;输入文件列在 [files] 节中。关于 .sby 文件语法的更多信息请参考 Reference for .sby file format,这里并不展开说明。mode provedepth 10[engines] smtbmc z3[script] read_verilog -formal hello.sv prep -top hello[files] hello.sv将上面的两个文件放在同一目录下,然后调用 sby 程序,即可获得证明结果。$ sby -f hello.sby...SBY 19:06:39[hello] engine_0.induction: finished (returncode=0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] engine_0: Status returned by engine for induction: pass...SBY 19:06:39 [hello] engine_0.basecase: finished (returncode=0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] engine_0: Status returned by engine for basecase: passSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: Elapsed clock time [H:MM:SS (secs)]: 0:00:00 (0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: Elapsed process time [H:MM:SS (secs)]: 0:00:00 (0)SBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: engine_0 (smtbmc z3) returned pass for inductionSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: engine_0 (smtbmc z3) returned pass for basecaseSBY 19:06:39 [hello] summary: successful proof by k-induction.SBY 19:06:39 [hello] DONE (PASS, rc=0) -
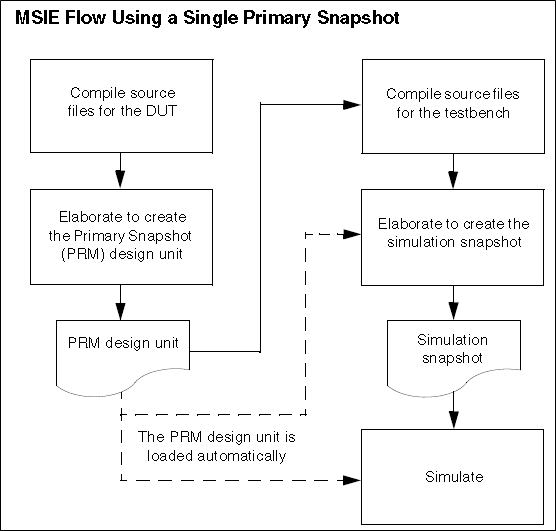
 cadence-irun(xrun) 增量编译 irun支持MSIE编译,MSIE的全称是 multi-snapshot incremental elaboration。将多个编译好的snapshot,组合成一个最终的snapshot,去仿真。利用这个技术,我们就可以使用irun来进行增量编译,从而节约编译时间。为了实现增量编译,我们将snapshot分为primary snapshot和incremental snapshot,primary snapshot指环境中不经常变化的代码,编译成的snapshot,incremental snapshot指环境中经常变化的代码,编译成的snapshot,最后再将这两个snapshot进行组合,得到最终的snapshot,去仿真。一、编译流程下图是单个primary snapshot的编译流程:将DUT,编译成primary snapshot,TB载入primary snapshot后,和tb一起进行编译,得到仿真的snapshot,再去仿真。下图是多个primary snapshot的编译流程:将SOC编译成primary snapshot,将IP编译成primary snapshot,将2个primary snapshot,和tb一起编译,得到最终的仿真snapshot,再进行仿真。二、实现方法一般情况下,我们是将DUT和TB进行分开编译,以实现增量编译。对于验证人员来说,DUT是不会变化的,因此我们可以将DUT,编译成primary snapshot,TB部分载入DUT的primary snapshot,和自己的TB代码一起编译,成最终的incremental snapshot,去仿真。这样,当环境修改之后,不需要重新编译RTL,这样,就节省了编译时间。特别是RTL的设计规模很大之后,这节约的时间,就更明显了。三、测试测试环境,组织结构如下:flist.rtl : 编译rtl的flistflist.tb : 编译tb的flistMakefiletop_tb.sv : testbench顶层source: 存放rtl code的目录uvm_code:存放tb code的目录1、makefile解析 Makefile内容如下:tc:= base_test_0 irun_prim: irun -sv -64bit -f flist.rtl -mkprimsnap -top uart_tx -l irun_rtl.log irun_inca: irun -c -sv -64bit -f flist.tb -uvm -uvmhome CDNS-1.2 -primtop uart_tx -l irun_tb.log irun_run: irun -R +UVM_TESTNAME=$(tc) -l irun_run.log clean: rm -rf INCA_libs rm -f *.log 对于 irun_prim 目标,根据RTL代码生成primary snapshot。-sv: 启动sv编译-64bit: 启动64位的irun-f flist.rtl : 指定编译RTL的flist-mkprimsnap: 生成primary snapshot-top: 指定RTL的顶层-l: 指定log文件对于 irun_inca 目标,载入RTL编译得到的primary snapshot,根据TB代码生成incremental snapshot, -c: 只编译,不仿真-f flist.tb: 指定编译TB的flist-uvm: 启动uvm编译-uvmhome CDNS-1.2: 指定uvm的home目录为irun工具目录下的UVM-1.2目录-primtop uart_tx: 指定需要载入primary snapshot的顶层。对于 irun_run 目标,仿真。-R : 不编译,直接仿真+UVM_TESTNAME: uvm指定testcase的选项2、第一次执行make irun_prim; 生成primary snapshotmake irun_inca: 载入primary snapshot,和tb一起编译生成incremantal snapshot。载入primary snapshot:生成incremantal snapshot。3、第二次执行此时,修改top_tb.sv的代码,增加一行打印。因为RTL没有编译,因此可以跳过编译RTL,直接make irun_inca。载入 primary snapshot,跳过了代码生成。生成incremantal snapshot。仿真,打印出hello。测试的RTL,规模比较小,感受不到增量编译的好处,但是当RTL的规模一旦变得很大,编译RTL就要花费数十分钟,此时,就可以体会到增量编译的好处了。在服务器,测试我们的环境,使用增量编译后,将编译时间,从5分钟,缩减到了20秒。https://www.cnblogs.com/david-wei0810/p/14177607.html
cadence-irun(xrun) 增量编译 irun支持MSIE编译,MSIE的全称是 multi-snapshot incremental elaboration。将多个编译好的snapshot,组合成一个最终的snapshot,去仿真。利用这个技术,我们就可以使用irun来进行增量编译,从而节约编译时间。为了实现增量编译,我们将snapshot分为primary snapshot和incremental snapshot,primary snapshot指环境中不经常变化的代码,编译成的snapshot,incremental snapshot指环境中经常变化的代码,编译成的snapshot,最后再将这两个snapshot进行组合,得到最终的snapshot,去仿真。一、编译流程下图是单个primary snapshot的编译流程:将DUT,编译成primary snapshot,TB载入primary snapshot后,和tb一起进行编译,得到仿真的snapshot,再去仿真。下图是多个primary snapshot的编译流程:将SOC编译成primary snapshot,将IP编译成primary snapshot,将2个primary snapshot,和tb一起编译,得到最终的仿真snapshot,再进行仿真。二、实现方法一般情况下,我们是将DUT和TB进行分开编译,以实现增量编译。对于验证人员来说,DUT是不会变化的,因此我们可以将DUT,编译成primary snapshot,TB部分载入DUT的primary snapshot,和自己的TB代码一起编译,成最终的incremental snapshot,去仿真。这样,当环境修改之后,不需要重新编译RTL,这样,就节省了编译时间。特别是RTL的设计规模很大之后,这节约的时间,就更明显了。三、测试测试环境,组织结构如下:flist.rtl : 编译rtl的flistflist.tb : 编译tb的flistMakefiletop_tb.sv : testbench顶层source: 存放rtl code的目录uvm_code:存放tb code的目录1、makefile解析 Makefile内容如下:tc:= base_test_0 irun_prim: irun -sv -64bit -f flist.rtl -mkprimsnap -top uart_tx -l irun_rtl.log irun_inca: irun -c -sv -64bit -f flist.tb -uvm -uvmhome CDNS-1.2 -primtop uart_tx -l irun_tb.log irun_run: irun -R +UVM_TESTNAME=$(tc) -l irun_run.log clean: rm -rf INCA_libs rm -f *.log 对于 irun_prim 目标,根据RTL代码生成primary snapshot。-sv: 启动sv编译-64bit: 启动64位的irun-f flist.rtl : 指定编译RTL的flist-mkprimsnap: 生成primary snapshot-top: 指定RTL的顶层-l: 指定log文件对于 irun_inca 目标,载入RTL编译得到的primary snapshot,根据TB代码生成incremental snapshot, -c: 只编译,不仿真-f flist.tb: 指定编译TB的flist-uvm: 启动uvm编译-uvmhome CDNS-1.2: 指定uvm的home目录为irun工具目录下的UVM-1.2目录-primtop uart_tx: 指定需要载入primary snapshot的顶层。对于 irun_run 目标,仿真。-R : 不编译,直接仿真+UVM_TESTNAME: uvm指定testcase的选项2、第一次执行make irun_prim; 生成primary snapshotmake irun_inca: 载入primary snapshot,和tb一起编译生成incremantal snapshot。载入primary snapshot:生成incremantal snapshot。3、第二次执行此时,修改top_tb.sv的代码,增加一行打印。因为RTL没有编译,因此可以跳过编译RTL,直接make irun_inca。载入 primary snapshot,跳过了代码生成。生成incremantal snapshot。仿真,打印出hello。测试的RTL,规模比较小,感受不到增量编译的好处,但是当RTL的规模一旦变得很大,编译RTL就要花费数十分钟,此时,就可以体会到增量编译的好处了。在服务器,测试我们的环境,使用增量编译后,将编译时间,从5分钟,缩减到了20秒。https://www.cnblogs.com/david-wei0810/p/14177607.html -
 Verilog-AMS 知识汇总 verilog-AMS数据类型 --- wrealWREAL 是Verilog-AMS支持的一种新的数值模型。WREAL的特殊之处在于它使用有限的浮点数值的点来模拟一条电路工作曲线。而SPICE和Verilog-A的计算结果是一条理论上可以无限精度,包含无限点的的曲线。从某种程度上,WREAL的实现方式类似于Fast-Spice的查表点工作模式,其目的是进一步简化仿真,从而支持更大规模的模拟系统仿真。 使用WREAL的最大好处是速度快。使用WREAL变量的模型在计算的时候无需使用SPICE迭代运算。它使用的是比较简单的,直接推导的函数来模仿模拟电路真正的工作情况。 相比SPICE和Verilog-A的模型必须使用SPICE仿真器的迭代运算,WREAL仿真器使用离散事件触发,就像数字仿真器那样。这给WREAL的计算上带来极大的速度优势。但同时,离散的计算模式使得WREA模型在含有反馈的电路中无法给出准确的结果。在普通电路中它也需要牺牲输出的精度。所以,WREAL并不适用于需要精确度量的模拟电路的模型中。 WREAL的一个问题是,它需要对真正的模拟电路的行为有一个非常好的预测。因为,WREAL的所有计算都是前向的,我们想要用这些前向计算来模拟SPICE仿真器迭代结算的结果,就需要对实际电路工作情况有个很好的了解。然而,模型通常在设计阶段的前期实现,而此时通常不会有很好的对真实电路的预测。如果WREAL模型无法很好的体现SPICE仿真器对真实电路的仿真结果,那模型的意义就不大了。亦或需要在设计后期随着真实电路的开发修改模型,这样就会牺牲一些研发的时间。 有一些相关的研究正在进行中,比如利用简单的电路生成WREAL模型,这样可以作为未来新项目系统的起始WREAL模型。也有一些研究包括迭代WREAL和真实电路仿真,这样可以自动修改WREAL模型等等。但不管怎么,对于WREAL在大规模需要精度的验证中的使用,还是需要一定考虑。 一、端口(Port) Port(端口),也被称为引脚或端子,被用来连接模块到其他模块。因此,端口就是电线。简单连接的端口声明是连接声明,其中关键字wire被以下方向说明符之一替换:input、output或inout。例如: module inv (out, in); output out; input in;assign out = ~in;endmodulemodule mux (out, in0, in1, sel); output [7:0] out; input [7:0] in0, in1; input sel;assign out = sel ? in1 : in0;endmodule 对于其他类型的连接,或者寄存器(寄存器只能作为输出声明),声明的前面简单地加上方向说明符: module counter (out, clk); output reg [3:0] out;initial out = 0;always @(posedge ckl) out = out + 1;endmodule 默认情况下,多位端口的内容被解释为无符号数(值被解释为正二进制数)。可以明确指定数字是被解释为有符号数还是无符号数,如下所示: input unsigned [3:0] gain;input signed [6:0] offset;在这种情况下,增益是无符号的,而偏移量是有符号的,这意味着它被解释为有符号的双补数。因此,如果增益= 4'bF,则其值解释为15,如果offset = 7'b7FF,则其值解释为-1。 If it is necessary to apply a discipline to a port, the port declaration should be repeated with direction specifier replaced by the discipline. For example: module buffer (out, in); output out; input in; electrical out, in;analog V(out) <+ V(in);endmodule Verilog还支持连续信号总线和wreal(必须声明为总线而不是数组): module mux (out, in, sel); output out; input [1:0] in; input sel; electrical out; electrical [1:0] in;analog begin @(sel); V(out) <+ transition(sel === 0, 0, 100n)*V(in[0]); V(out) <+ transition(sel === 1, 0, 100n)*V(in[1]);endendmodulemodule mux (out, in, sel); output wreal out; input wreal [1:0] in; input sel;assign out = sel ? in[1] : in[0];endmodule Note:The Cadence simulator does not seem to follow the standard when it comes to declaring buses of wreals. With the Cadence simulator you should declare buses of wreals as arrays rather than as buses: module mux (out, in, sel); output wreal out; input wreal in[1:0]; input sel;assign out = sel ? in[1] : in[0];endmodule———————————————— 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gsjthxy/article/details/107618649
Verilog-AMS 知识汇总 verilog-AMS数据类型 --- wrealWREAL 是Verilog-AMS支持的一种新的数值模型。WREAL的特殊之处在于它使用有限的浮点数值的点来模拟一条电路工作曲线。而SPICE和Verilog-A的计算结果是一条理论上可以无限精度,包含无限点的的曲线。从某种程度上,WREAL的实现方式类似于Fast-Spice的查表点工作模式,其目的是进一步简化仿真,从而支持更大规模的模拟系统仿真。 使用WREAL的最大好处是速度快。使用WREAL变量的模型在计算的时候无需使用SPICE迭代运算。它使用的是比较简单的,直接推导的函数来模仿模拟电路真正的工作情况。 相比SPICE和Verilog-A的模型必须使用SPICE仿真器的迭代运算,WREAL仿真器使用离散事件触发,就像数字仿真器那样。这给WREAL的计算上带来极大的速度优势。但同时,离散的计算模式使得WREA模型在含有反馈的电路中无法给出准确的结果。在普通电路中它也需要牺牲输出的精度。所以,WREAL并不适用于需要精确度量的模拟电路的模型中。 WREAL的一个问题是,它需要对真正的模拟电路的行为有一个非常好的预测。因为,WREAL的所有计算都是前向的,我们想要用这些前向计算来模拟SPICE仿真器迭代结算的结果,就需要对实际电路工作情况有个很好的了解。然而,模型通常在设计阶段的前期实现,而此时通常不会有很好的对真实电路的预测。如果WREAL模型无法很好的体现SPICE仿真器对真实电路的仿真结果,那模型的意义就不大了。亦或需要在设计后期随着真实电路的开发修改模型,这样就会牺牲一些研发的时间。 有一些相关的研究正在进行中,比如利用简单的电路生成WREAL模型,这样可以作为未来新项目系统的起始WREAL模型。也有一些研究包括迭代WREAL和真实电路仿真,这样可以自动修改WREAL模型等等。但不管怎么,对于WREAL在大规模需要精度的验证中的使用,还是需要一定考虑。 一、端口(Port) Port(端口),也被称为引脚或端子,被用来连接模块到其他模块。因此,端口就是电线。简单连接的端口声明是连接声明,其中关键字wire被以下方向说明符之一替换:input、output或inout。例如: module inv (out, in); output out; input in;assign out = ~in;endmodulemodule mux (out, in0, in1, sel); output [7:0] out; input [7:0] in0, in1; input sel;assign out = sel ? in1 : in0;endmodule 对于其他类型的连接,或者寄存器(寄存器只能作为输出声明),声明的前面简单地加上方向说明符: module counter (out, clk); output reg [3:0] out;initial out = 0;always @(posedge ckl) out = out + 1;endmodule 默认情况下,多位端口的内容被解释为无符号数(值被解释为正二进制数)。可以明确指定数字是被解释为有符号数还是无符号数,如下所示: input unsigned [3:0] gain;input signed [6:0] offset;在这种情况下,增益是无符号的,而偏移量是有符号的,这意味着它被解释为有符号的双补数。因此,如果增益= 4'bF,则其值解释为15,如果offset = 7'b7FF,则其值解释为-1。 If it is necessary to apply a discipline to a port, the port declaration should be repeated with direction specifier replaced by the discipline. For example: module buffer (out, in); output out; input in; electrical out, in;analog V(out) <+ V(in);endmodule Verilog还支持连续信号总线和wreal(必须声明为总线而不是数组): module mux (out, in, sel); output out; input [1:0] in; input sel; electrical out; electrical [1:0] in;analog begin @(sel); V(out) <+ transition(sel === 0, 0, 100n)*V(in[0]); V(out) <+ transition(sel === 1, 0, 100n)*V(in[1]);endendmodulemodule mux (out, in, sel); output wreal out; input wreal [1:0] in; input sel;assign out = sel ? in[1] : in[0];endmodule Note:The Cadence simulator does not seem to follow the standard when it comes to declaring buses of wreals. With the Cadence simulator you should declare buses of wreals as arrays rather than as buses: module mux (out, in, sel); output wreal out; input wreal in[1:0]; input sel;assign out = sel ? in[1] : in[0];endmodule———————————————— 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gsjthxy/article/details/107618649 -
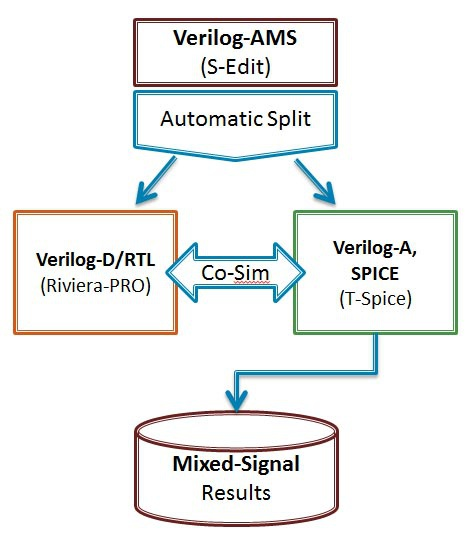
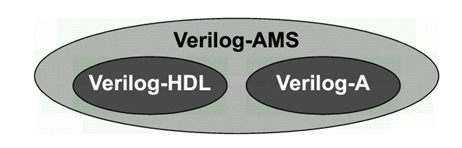
 Verilog-AMS Verilog-A介绍 最近浅学了一下Verilog-AMS和Verilog-A的语法,记录一下自己理解:.Verilog-A是Verilog-AMS的子集,Verilog-A是只对analog电路进行建模的(运行基于Spice仿真器),而Verilog-AMS则可以对mixed- signal电路进行建模,包括了数字Verilog和Veirlog-A的语法 (运行基于 AMS混合信号仿真器).对于Verilog-A来说,其端口都是电器属性的,即类似于你从Spice里看到的那些模型一样;.对于Verilog-AMS来说,可以有logic类型的数字端口输入,然后electrical类型的模拟端口输出等等;.Verilog-AMS/A 可以从行为级和电路级对电路进行建模,简化了对于系统电路仿真时的复杂性;veirlog-AMS/Verilog-A中的关键概念:.分立信号转化为连续的信号 (对于数字只有0,1两种状态,但转化为连续信号,0->1过程值也会存在);.事件发生来触发信号变化(基于添加时间戳)(需解决设置的变量在事件未触发之前的初值问题);.在Verilog-A中,要时刻考虑Vth的特性,注意基于Verilog-A的model写法!.事件触发原理:在连续仿真器中,在发生事件处放置一个时间标记,从而将离散的仿真连续化;.model概念,branch概念,testbench概念(类似于verilog);一些关键代码:0. Verilog-A的阈值电压检测标准代码 (基于反相器):module inverter(out, in):output out;input in;electrical out, in;integer d_in; analog begin @(cross(V(in) - 0.5*V(vdd))) //穿越阈值电压写法(event statement),作用是在这个点建立时间戳,方便仿真器进行捕捉,否则捕捉不到这里发生的突变 ; //空白行,不在event发生时执行特定命令 d_in = V(in) > 0.5*V(vdd); //建立方波 V(out) <+ transition(!d_in, 0, 10n)*V(vdd); //用transition进行smooth处理 end endmodule.Model DAC (关键:electrical digital input -> (Vth) -> integer -> electrical analog differential output)module dac (out_p, out_n, in, clock, enable, vdda, gnda); output out_p, out_n; electrical out_p, out_n; input [7:0] in; electrical [7:0] in; input clock; electrical clock; input enable; electrical enable; input vdda; electrical vdda; input gnda; electrical gnda; integer code, en; real value;genvar i; analog begin // convert the input to a signed integer on positive clock edge @(cross(V(clock) - V(vdda)/2), +1) begin code = 0; for (i = 0; i < 8; i = i + 1) begin @(cross(V(in[i]) - V(vdda)/2)); if (V(in[i]) > V(vdda)/2) code = code + (1 << i); if (code >= 128) code = code - 256; value = code/256.0; end // reset output value when disabled @(cross(V(enable) - V(vdda)/2)) ; if (V(enable) < V(vdda)/2) value = 0; // drive the differential output V(out_p) <+ V(vdda)/2 + transition(value/2, 0, 10n); V(out_n) <+ V(vdda)/2 - transition(value/2, 0, 10n); end endmodule2. Model ADC (关键:electrical analog input -> (vth) -> integer -> electrical digital output)module adc (out, in, clk); output [5:0] out; input in, clk; electrical [5:0] out; electrical in, clk; parameter real vh = 1; parameter real vth = vh/2; parameter real tt = 100n from (0:inf); integer result; genvar i; analog begin @(cross(V(clk) - vth, +1)) begin result = 64*(V(in)+1)/2; if (result > 63) result = 63; else if (result < 0) result = 0; end for (i=0; i<6; i=i+1) V(out[i]) <+ transition(result & (1<<i) ? vh : 0, 0, tt); end endmodule3. Model Multiplexer: (关键:[3:0] sel 可以直接放入 @()中)module(out, in, sel); output out; electrical out; input [3:0] in; electrical [3:0] in; input [3:0] sel; logic [3:0] sel; analog begin @(sel) ; V(out) <+ V(in[0])*transition(sel === 0, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[1])*transition(sel === 1, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[2])*transition(sel === 2, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[3])*transition(sel === 3, 0, 100n); end endmodule4. 对于Cadence语法限制的标准处理方法:(Unfortunately, the Cadence simulator places unreasonable restrictions on event expressions in the analog block. Specifically, any digital signals used in an analog event expression must be preceded by either the posedge or negedge qualifiers. Thus, the model must be modified when intended for the Cadence simulator: )module cp (out, u, d): output out; electrical out; input u, d; logic u, d; reg sync = 0; always @(u or d) sync <= !sync; analog begin @(posedge sync or negedge sync) ; I(out) <+ 10u*(transition(d, 0, 1n) - transition(u, 0, 1n)); end endmodulean example of writing in Cadence:Cadence’s AMS simulator only supports discrete transitions filtered through posedge or negedge. Putting a discrete wire, discrete variable, or named event directly in a continuous event statement is not supported (as of 2014).real vgain;always @(gain) vgain = pow(10, (gain - 32.0)/20); real voffset;always @(offset) voffset = 1m*offset; reg break = 0;always @(vgain or voffset or en) break <= break; analog begin @(posedge break or negedge break) ; V(out) <+ transition(en ? vgain : 0, 0, 100n) * V(in) + voffset; endWith Cadence’s simulator, you can use the following for modeling multiplexers:module(out, in, sel); output out; electrical out; input [3:0] in; electrical [3:0] in; input [3:0] sel; logic [3:0] sel; reg sync = 0; always @(sel) sync <= !sync; analog begin @(posedge sync or negedge sync) ; V(out) <+ V(in[0])*transition(sel === 0, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[1])*transition(sel === 1, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[2])*transition(sel === 2, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[3])*transition(sel === 3, 0, 100n); end endmoduleTo implement a Verilog-A version of a multiplexer:module(out, in, sel); output out; electrical out; input [3:0] in; electrical [3:0] in; input [3:0] sel; logic [3:0] sel; parameter real vdd = 2.5; integer SEL; genvar i; analog begin // convert the input to an integer SEL = 0; for (i = 0; i < 2; i = i + 1) begin @(cross(V(sel[i]) - vdd/2)); if (V(sel[i]) > vdd/2) SEL = SEL + (1 << i); end V(out) <+ V(in[0])*transition(SEL == 0, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[1])*transition(SEL == 1, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[2])*transition(SEL == 2, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[3])*transition(SEL == 3, 0, 100n); end endmodule
Verilog-AMS Verilog-A介绍 最近浅学了一下Verilog-AMS和Verilog-A的语法,记录一下自己理解:.Verilog-A是Verilog-AMS的子集,Verilog-A是只对analog电路进行建模的(运行基于Spice仿真器),而Verilog-AMS则可以对mixed- signal电路进行建模,包括了数字Verilog和Veirlog-A的语法 (运行基于 AMS混合信号仿真器).对于Verilog-A来说,其端口都是电器属性的,即类似于你从Spice里看到的那些模型一样;.对于Verilog-AMS来说,可以有logic类型的数字端口输入,然后electrical类型的模拟端口输出等等;.Verilog-AMS/A 可以从行为级和电路级对电路进行建模,简化了对于系统电路仿真时的复杂性;veirlog-AMS/Verilog-A中的关键概念:.分立信号转化为连续的信号 (对于数字只有0,1两种状态,但转化为连续信号,0->1过程值也会存在);.事件发生来触发信号变化(基于添加时间戳)(需解决设置的变量在事件未触发之前的初值问题);.在Verilog-A中,要时刻考虑Vth的特性,注意基于Verilog-A的model写法!.事件触发原理:在连续仿真器中,在发生事件处放置一个时间标记,从而将离散的仿真连续化;.model概念,branch概念,testbench概念(类似于verilog);一些关键代码:0. Verilog-A的阈值电压检测标准代码 (基于反相器):module inverter(out, in):output out;input in;electrical out, in;integer d_in; analog begin @(cross(V(in) - 0.5*V(vdd))) //穿越阈值电压写法(event statement),作用是在这个点建立时间戳,方便仿真器进行捕捉,否则捕捉不到这里发生的突变 ; //空白行,不在event发生时执行特定命令 d_in = V(in) > 0.5*V(vdd); //建立方波 V(out) <+ transition(!d_in, 0, 10n)*V(vdd); //用transition进行smooth处理 end endmodule.Model DAC (关键:electrical digital input -> (Vth) -> integer -> electrical analog differential output)module dac (out_p, out_n, in, clock, enable, vdda, gnda); output out_p, out_n; electrical out_p, out_n; input [7:0] in; electrical [7:0] in; input clock; electrical clock; input enable; electrical enable; input vdda; electrical vdda; input gnda; electrical gnda; integer code, en; real value;genvar i; analog begin // convert the input to a signed integer on positive clock edge @(cross(V(clock) - V(vdda)/2), +1) begin code = 0; for (i = 0; i < 8; i = i + 1) begin @(cross(V(in[i]) - V(vdda)/2)); if (V(in[i]) > V(vdda)/2) code = code + (1 << i); if (code >= 128) code = code - 256; value = code/256.0; end // reset output value when disabled @(cross(V(enable) - V(vdda)/2)) ; if (V(enable) < V(vdda)/2) value = 0; // drive the differential output V(out_p) <+ V(vdda)/2 + transition(value/2, 0, 10n); V(out_n) <+ V(vdda)/2 - transition(value/2, 0, 10n); end endmodule2. Model ADC (关键:electrical analog input -> (vth) -> integer -> electrical digital output)module adc (out, in, clk); output [5:0] out; input in, clk; electrical [5:0] out; electrical in, clk; parameter real vh = 1; parameter real vth = vh/2; parameter real tt = 100n from (0:inf); integer result; genvar i; analog begin @(cross(V(clk) - vth, +1)) begin result = 64*(V(in)+1)/2; if (result > 63) result = 63; else if (result < 0) result = 0; end for (i=0; i<6; i=i+1) V(out[i]) <+ transition(result & (1<<i) ? vh : 0, 0, tt); end endmodule3. Model Multiplexer: (关键:[3:0] sel 可以直接放入 @()中)module(out, in, sel); output out; electrical out; input [3:0] in; electrical [3:0] in; input [3:0] sel; logic [3:0] sel; analog begin @(sel) ; V(out) <+ V(in[0])*transition(sel === 0, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[1])*transition(sel === 1, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[2])*transition(sel === 2, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[3])*transition(sel === 3, 0, 100n); end endmodule4. 对于Cadence语法限制的标准处理方法:(Unfortunately, the Cadence simulator places unreasonable restrictions on event expressions in the analog block. Specifically, any digital signals used in an analog event expression must be preceded by either the posedge or negedge qualifiers. Thus, the model must be modified when intended for the Cadence simulator: )module cp (out, u, d): output out; electrical out; input u, d; logic u, d; reg sync = 0; always @(u or d) sync <= !sync; analog begin @(posedge sync or negedge sync) ; I(out) <+ 10u*(transition(d, 0, 1n) - transition(u, 0, 1n)); end endmodulean example of writing in Cadence:Cadence’s AMS simulator only supports discrete transitions filtered through posedge or negedge. Putting a discrete wire, discrete variable, or named event directly in a continuous event statement is not supported (as of 2014).real vgain;always @(gain) vgain = pow(10, (gain - 32.0)/20); real voffset;always @(offset) voffset = 1m*offset; reg break = 0;always @(vgain or voffset or en) break <= break; analog begin @(posedge break or negedge break) ; V(out) <+ transition(en ? vgain : 0, 0, 100n) * V(in) + voffset; endWith Cadence’s simulator, you can use the following for modeling multiplexers:module(out, in, sel); output out; electrical out; input [3:0] in; electrical [3:0] in; input [3:0] sel; logic [3:0] sel; reg sync = 0; always @(sel) sync <= !sync; analog begin @(posedge sync or negedge sync) ; V(out) <+ V(in[0])*transition(sel === 0, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[1])*transition(sel === 1, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[2])*transition(sel === 2, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[3])*transition(sel === 3, 0, 100n); end endmoduleTo implement a Verilog-A version of a multiplexer:module(out, in, sel); output out; electrical out; input [3:0] in; electrical [3:0] in; input [3:0] sel; logic [3:0] sel; parameter real vdd = 2.5; integer SEL; genvar i; analog begin // convert the input to an integer SEL = 0; for (i = 0; i < 2; i = i + 1) begin @(cross(V(sel[i]) - vdd/2)); if (V(sel[i]) > vdd/2) SEL = SEL + (1 << i); end V(out) <+ V(in[0])*transition(SEL == 0, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[1])*transition(SEL == 1, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[2])*transition(SEL == 2, 0, 100n); V(out) <+ V(in[3])*transition(SEL == 3, 0, 100n); end endmodule -
 vcs排除覆盖率虚高的方法 Synopsys vcs仿真器在收集覆盖率是怎么排除仿真glitch产生的覆盖率数据?在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,可以通过设置一些选项和参数来排除仿真glitch产生的覆盖率数据。以下是一些建议:使用-coverage exclude_glblck glitch选项:此选项将忽略由于glitch引起的全局时钟块的覆盖率。设置适当的仿真步长:使用较小的仿真步长可能会导致更多的glitch。尝试增加仿真步长以减少glitch的可能性。使用-vcs+lic+nowarn+assert选项:此选项会关闭所有警告,并启用所有的断言。这有助于捕获可能导致glitch的错误条件。调整覆盖率收集频率:通过调整-cm linecover或-cm togglecover等选项的频率,可以减少glitch的影响。在代码中添加额外的检查:如果可能,可以在设计代码中添加额外的检查,以确保信号稳定后再进行覆盖率收集。分析覆盖率报告:查看覆盖率报告并识别哪些区域可能存在glitch。然后,可以在这些区域中添加额外的测试用例,以更好地覆盖这些情况。请注意,这些方法可能无法完全消除由glitch引起的覆盖率数据问题,但它们可以帮助减少此类问题的发生。在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,排除由于glitch(瞬时信号跳变)产生的覆盖率数据可以通过使用特定的编译和仿真选项来实现。以下是一些方法,这些方法基于上述文档中的信息:1.使用-cm_glitch选项:这个选项可以用来过滤掉由于glitch导致的额外夏盖率数据。例如,设置-cm_glitch 0可以过滤掉在0时刻由于glitchi产生的夏盖率数据。2.利用$cm_coverage系统函数:在Verilog:或SystemVerilog代码中,可以通过$cm_coverage系统函数动态地查询或修改夏盖率选项。这个函数可以用来在运行时使能或关闭特定的夏盖率类型,从而避免收集由于gtch产生的夏盖率数据3。3.设置-covg_cont_on_error选项:当仿真运行到非法功能夏盖率bin时,使用这个选项可以让仿真继续运行,而不是停止。这样可以避免由于错误或异常情况导致的覆盖率数据被错误地收集。通过上述方法,用户可以有效地排除由于gtc产生的夏盖率数据,确保覆盖率结果的准确性和可靠性。这些选项和函数提供了灵活性,使得覆盖率收集可以专注于用户感兴趣的特定仿真行为和事件,同时避免由于仿真过程中的瞬时信号跳变而引入的噪声。Synopsys vcs仿真器在收集覆盖率是怎么排除仿真0时刻的覆盖率数据在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,可以通过以下方法来排除仿真0时刻的覆盖率数据:使用-cm_init选项:此选项允许您指定一个时间点(以模拟周期为单位),从该时间点开始收集覆盖率数据。例如,如果您希望从第一个时钟边沿开始收集覆盖率数据,可以使用以下命令:-cm_init=1这将忽略仿真开始时的0时刻覆盖率数据。使用条件覆盖率:您可以使用条件覆盖率(CCOV)选项来控制何时开始收集覆盖率数据。通过在设计代码中添加相应的条件语句,可以在满足特定条件后开始收集覆盖率数据。例如:initial begin @(posedge clk); if (reset == 1'b0) begin $set_coverage_control("start"); end end在代码中添加额外的检查:如果可能,可以在设计代码中添加额外的检查,以确保信号稳定后再进行覆盖率收集。这可以帮助避免在仿真开始时收集不准确的覆盖率数据。请注意,这些方法可能无法完全消除由仿真0时刻引起的覆盖率数据问题,但它们可以帮助减少此类问题的发生。当然,以下是更多关于如何在Synopsys VCS仿真器中排除仿真0时刻的覆盖率数据的方法:使用延迟初始化(Deferred Initialization):通过使用VCS的延迟初始化功能,可以在仿真开始时避免某些模块或信号被初始化。这可以帮助确保在收集覆盖率数据之前,所有必要的信号和模块都已经稳定。分析覆盖率报告:查看覆盖率报告并识别哪些区域可能存在由于仿真0时刻导致的问题。然后,可以针对这些区域编写额外的测试用例,以更好地覆盖这些情况。使用-cm_control选项:此选项允许您控制何时开始和停止收集覆盖率数据。您可以根据需要创建多个覆盖组,并为每个组设置不同的起始和结束时间点。例如:-cm_control "start_group1:2; end_group1:3" -cm_control "start_group2:5; end_group2:7"调整仿真步长:尝试增加仿真步长以减少由仿真0时刻引起的不准确的覆盖率数据。验证设计代码:检查您的设计代码,确保在仿真开始时没有触发任何不应发生的事件或状态变化。这可能包括复位、中断或其他可能导致覆盖率数据问题的条件。请记住,这些方法可能会有所帮助,但可能无法完全消除由仿真0时刻引起的覆盖率数据问题。在实际应用中,您可能需要结合多种方法来优化覆盖率数据的质量。在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,排除仿真0时刻的夏盖率数据可以通过设置特定的编译和仿真选项来实现。以下是一些方法和选项,这些方法基于上述文档中的信息:1.使用编译选项-cmhier来指定要收集覆盖率的模块、实例和子层次结构,以及要排除的源文件。例如,如果你想排除某个模块及其子模块的夏盖率,可以在-cm_hier配置文件中使用+tree instance_name[level_number]来指定只编译和收集夏盖率的实例和子实例,而忽略其他实例1。2.利用仿真选项-cm来控制覆盖率的收集。例如,如果你想排除0时刻的某些wys块的夏盖率,可以通过设置-cm选项来指定不收集特定类型的覆盖率,如tg1(翻转覆盖率)或1ine(代码行覆盖本)3.使用系统函数$cm_coverage()在仿真过程中动态地开启或关闭覆盖率的收集。通过在仿真脚本中设置条件,可以在0时刻之后开启夏盖率收集,从而排除0时刻的覆盖率数据1。4.在仿真脚本中设置条件,以确保在0时刻不执行某些测试用例或测试序列,这样可以避免在0时刻收集到不希望的夏盖率数据。5.使用urg命令行工具来合并覆盖率数据时,可以通过-dbname选项指定要合并的覆盖率数据库文件,而不包括0时刻的数据。此外,可以使用-orep0rt选项来阻止生成包含0时刻数据的夏盖率报告。通过上述方法,用户可以根据需要排除仿真0时刻的夏盖率数据,以便更准确地分析和评估仿真结果。这些方法提供了灵活性,使得覆盖率收集可以专注于用户感兴趣的特定仿真行为和事件。
vcs排除覆盖率虚高的方法 Synopsys vcs仿真器在收集覆盖率是怎么排除仿真glitch产生的覆盖率数据?在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,可以通过设置一些选项和参数来排除仿真glitch产生的覆盖率数据。以下是一些建议:使用-coverage exclude_glblck glitch选项:此选项将忽略由于glitch引起的全局时钟块的覆盖率。设置适当的仿真步长:使用较小的仿真步长可能会导致更多的glitch。尝试增加仿真步长以减少glitch的可能性。使用-vcs+lic+nowarn+assert选项:此选项会关闭所有警告,并启用所有的断言。这有助于捕获可能导致glitch的错误条件。调整覆盖率收集频率:通过调整-cm linecover或-cm togglecover等选项的频率,可以减少glitch的影响。在代码中添加额外的检查:如果可能,可以在设计代码中添加额外的检查,以确保信号稳定后再进行覆盖率收集。分析覆盖率报告:查看覆盖率报告并识别哪些区域可能存在glitch。然后,可以在这些区域中添加额外的测试用例,以更好地覆盖这些情况。请注意,这些方法可能无法完全消除由glitch引起的覆盖率数据问题,但它们可以帮助减少此类问题的发生。在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,排除由于glitch(瞬时信号跳变)产生的覆盖率数据可以通过使用特定的编译和仿真选项来实现。以下是一些方法,这些方法基于上述文档中的信息:1.使用-cm_glitch选项:这个选项可以用来过滤掉由于glitch导致的额外夏盖率数据。例如,设置-cm_glitch 0可以过滤掉在0时刻由于glitchi产生的夏盖率数据。2.利用$cm_coverage系统函数:在Verilog:或SystemVerilog代码中,可以通过$cm_coverage系统函数动态地查询或修改夏盖率选项。这个函数可以用来在运行时使能或关闭特定的夏盖率类型,从而避免收集由于gtch产生的夏盖率数据3。3.设置-covg_cont_on_error选项:当仿真运行到非法功能夏盖率bin时,使用这个选项可以让仿真继续运行,而不是停止。这样可以避免由于错误或异常情况导致的覆盖率数据被错误地收集。通过上述方法,用户可以有效地排除由于gtc产生的夏盖率数据,确保覆盖率结果的准确性和可靠性。这些选项和函数提供了灵活性,使得覆盖率收集可以专注于用户感兴趣的特定仿真行为和事件,同时避免由于仿真过程中的瞬时信号跳变而引入的噪声。Synopsys vcs仿真器在收集覆盖率是怎么排除仿真0时刻的覆盖率数据在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,可以通过以下方法来排除仿真0时刻的覆盖率数据:使用-cm_init选项:此选项允许您指定一个时间点(以模拟周期为单位),从该时间点开始收集覆盖率数据。例如,如果您希望从第一个时钟边沿开始收集覆盖率数据,可以使用以下命令:-cm_init=1这将忽略仿真开始时的0时刻覆盖率数据。使用条件覆盖率:您可以使用条件覆盖率(CCOV)选项来控制何时开始收集覆盖率数据。通过在设计代码中添加相应的条件语句,可以在满足特定条件后开始收集覆盖率数据。例如:initial begin @(posedge clk); if (reset == 1'b0) begin $set_coverage_control("start"); end end在代码中添加额外的检查:如果可能,可以在设计代码中添加额外的检查,以确保信号稳定后再进行覆盖率收集。这可以帮助避免在仿真开始时收集不准确的覆盖率数据。请注意,这些方法可能无法完全消除由仿真0时刻引起的覆盖率数据问题,但它们可以帮助减少此类问题的发生。当然,以下是更多关于如何在Synopsys VCS仿真器中排除仿真0时刻的覆盖率数据的方法:使用延迟初始化(Deferred Initialization):通过使用VCS的延迟初始化功能,可以在仿真开始时避免某些模块或信号被初始化。这可以帮助确保在收集覆盖率数据之前,所有必要的信号和模块都已经稳定。分析覆盖率报告:查看覆盖率报告并识别哪些区域可能存在由于仿真0时刻导致的问题。然后,可以针对这些区域编写额外的测试用例,以更好地覆盖这些情况。使用-cm_control选项:此选项允许您控制何时开始和停止收集覆盖率数据。您可以根据需要创建多个覆盖组,并为每个组设置不同的起始和结束时间点。例如:-cm_control "start_group1:2; end_group1:3" -cm_control "start_group2:5; end_group2:7"调整仿真步长:尝试增加仿真步长以减少由仿真0时刻引起的不准确的覆盖率数据。验证设计代码:检查您的设计代码,确保在仿真开始时没有触发任何不应发生的事件或状态变化。这可能包括复位、中断或其他可能导致覆盖率数据问题的条件。请记住,这些方法可能会有所帮助,但可能无法完全消除由仿真0时刻引起的覆盖率数据问题。在实际应用中,您可能需要结合多种方法来优化覆盖率数据的质量。在Synopsys VCS仿真器中,排除仿真0时刻的夏盖率数据可以通过设置特定的编译和仿真选项来实现。以下是一些方法和选项,这些方法基于上述文档中的信息:1.使用编译选项-cmhier来指定要收集覆盖率的模块、实例和子层次结构,以及要排除的源文件。例如,如果你想排除某个模块及其子模块的夏盖率,可以在-cm_hier配置文件中使用+tree instance_name[level_number]来指定只编译和收集夏盖率的实例和子实例,而忽略其他实例1。2.利用仿真选项-cm来控制覆盖率的收集。例如,如果你想排除0时刻的某些wys块的夏盖率,可以通过设置-cm选项来指定不收集特定类型的覆盖率,如tg1(翻转覆盖率)或1ine(代码行覆盖本)3.使用系统函数$cm_coverage()在仿真过程中动态地开启或关闭覆盖率的收集。通过在仿真脚本中设置条件,可以在0时刻之后开启夏盖率收集,从而排除0时刻的覆盖率数据1。4.在仿真脚本中设置条件,以确保在0时刻不执行某些测试用例或测试序列,这样可以避免在0时刻收集到不希望的夏盖率数据。5.使用urg命令行工具来合并覆盖率数据时,可以通过-dbname选项指定要合并的覆盖率数据库文件,而不包括0时刻的数据。此外,可以使用-orep0rt选项来阻止生成包含0时刻数据的夏盖率报告。通过上述方法,用户可以根据需要排除仿真0时刻的夏盖率数据,以便更准确地分析和评估仿真结果。这些方法提供了灵活性,使得覆盖率收集可以专注于用户感兴趣的特定仿真行为和事件。