搜索到
378
篇与
的结果
-
 模拟电路中的蒙特卡洛仿真 核心定义蒙特卡洛仿真是一种基于统计学和随机抽样的计算方法,用于分析和预测电路性能在制造工艺波动影响下的变化情况。简单来说,它就像是在计算机上对芯片进行“海量次数的虚拟生产”。在每次“生产”中,仿真器会随机改变电路中各个元器件(如晶体管、电阻、电容)的参数(例如阈值电压、沟道长度、电阻值等),这些变化是基于实际的工艺偏差统计模型。然后,仿真器对每一个“生产”出来的电路样本进行完整的性能测试(如增益、带宽、功耗等)。通过分析成千上万次这样的随机抽样结果,工程师就能得到电路性能的统计分布,从而评估其良率和鲁棒性。为什么需要蒙特卡洛仿真?在理想的数学模型中,所有晶体管的参数都是完全一致且精确的。但在现实世界的半导体制造过程中,由于光刻、刻蚀、离子注入等步骤的微小随机波动,即使是同一晶圆上相邻的两个晶体管,其物理参数(如栅氧厚度、掺杂浓度、沟道长度)也会存在细微差异。这些差异被称为工艺偏差。如果只进行“典型值”仿真(即所有元件都使用标称值),设计出的电路可能在理论上完美,但一旦投入生产,大量芯片的性能会不达标,导致良率极低。蒙特卡洛仿真就是为了解决这个问题而生的,它回答了以下关键问题:成品率:在工艺波动下,有多少比例的芯片能同时满足所有性能指标?(例如,增益 > 80dB 且功耗 < 5mW 的芯片占多少?)性能分布:关键性能指标(如带宽、失调电压)的范围是多少?最坏情况是怎样的?设计裕量:当前的设计距离性能失效的边界还有多远?是否足够安全?敏感性分析:电路的性能对哪些元器件的参数变化最敏感?蒙特卡洛仿真如何工作?其工作流程可以概括为以下几个步骤:建立模型:这是基础。晶圆厂会提供包含工艺偏差信息的PDK。PDK中的器件模型(如BSIM模型)不仅包含典型值,还包含了每个参数的标准差(σ)和分布类型(通常是高斯分布/正态分布)。例如,一个电阻的标称值是1kΩ,其标准差可能是50Ω。设置仿真:工程师在仿真工具(如Cadence Spectre, Synopsys HSPICE等)中设置一个普通的电路性能测试(如直流工作点、瞬态分析、交流分析)。定义运行次数:工程师指定蒙特卡洛仿真的次数,例如500次或1000次。次数越多,统计结果越准确,但计算时间也越长。随机抽样与循环仿真:仿真器开始第一次循环。它根据PDK中的统计模型,为电路中的每一个元件随机生成一套参数值(例如,这次循环中某个NMOS的Vth比标称值高了0.5mV,另一个电阻的阻值低了1%)。用这套随机参数对整个电路进行一次完整的性能仿真,并记录结果(如增益=79.8dB)。重复上述过程,直到达到指定的运行次数。每一次循环都相当于“生产”并“测试”了一个新的电路样本。结果分析:仿真完成后,工具会生成所有性能指标的统计报告和图表,例如:直方图:直观显示性能(如增益)的分布情况。理想情况下,它应该是一个集中在设计目标附近的正态分布曲线。统计摘要:给出平均值(mean)、标准差(sigma)、最小值(min)、最大值(max)以及指定西格玛水平(如3σ)下的数值。散点图:分析两个性能参数之间的相关性(例如,增益高的样本是否功耗也更大?)。一个简单的例子:差分对失调电压假设你设计了一个运算放大器的输入差分对。在理想情况下,两个完全相同的晶体管输入相同的电压,输出差应为零(失调电压Vos=0)。但在蒙特卡洛仿真中,仿真器会随机改变两个晶体管的阈值电压(Vth)、尺寸(W/L)等参数。每次仿真都会得到一个非零的失调电压。运行1000次后,你可能会发现:失调电压的平均值接近0。失调电压呈正态分布。99.7%的样本(3σ范围)的失调电压在±2mV以内。这样,你就可以非常有信心地对外宣称:“我的运放设计在3σ水平下的失调电压小于2mV”。总结方面 解释本质 一种基于随机抽样的统计分析方法。目的 评估工艺偏差对电路性能的影响,预测成品率和鲁棒性。输入 带有工艺偏差统计模型的电路网表和器件模型(来自PDK)。输出 电路性能的统计分布(直方图)、平均值、标准差、最坏情况值等。重要性 是现代模拟/混合信号芯片设计不可或缺的一环,是连接理想设计与现实制造的关键桥梁,确保设计能在大规模生产中保持高良率。因此,蒙特卡洛仿真是模拟电路设计师评估其设计在实际生产中是否“可靠”和“健壮”的最重要工具之一。
模拟电路中的蒙特卡洛仿真 核心定义蒙特卡洛仿真是一种基于统计学和随机抽样的计算方法,用于分析和预测电路性能在制造工艺波动影响下的变化情况。简单来说,它就像是在计算机上对芯片进行“海量次数的虚拟生产”。在每次“生产”中,仿真器会随机改变电路中各个元器件(如晶体管、电阻、电容)的参数(例如阈值电压、沟道长度、电阻值等),这些变化是基于实际的工艺偏差统计模型。然后,仿真器对每一个“生产”出来的电路样本进行完整的性能测试(如增益、带宽、功耗等)。通过分析成千上万次这样的随机抽样结果,工程师就能得到电路性能的统计分布,从而评估其良率和鲁棒性。为什么需要蒙特卡洛仿真?在理想的数学模型中,所有晶体管的参数都是完全一致且精确的。但在现实世界的半导体制造过程中,由于光刻、刻蚀、离子注入等步骤的微小随机波动,即使是同一晶圆上相邻的两个晶体管,其物理参数(如栅氧厚度、掺杂浓度、沟道长度)也会存在细微差异。这些差异被称为工艺偏差。如果只进行“典型值”仿真(即所有元件都使用标称值),设计出的电路可能在理论上完美,但一旦投入生产,大量芯片的性能会不达标,导致良率极低。蒙特卡洛仿真就是为了解决这个问题而生的,它回答了以下关键问题:成品率:在工艺波动下,有多少比例的芯片能同时满足所有性能指标?(例如,增益 > 80dB 且功耗 < 5mW 的芯片占多少?)性能分布:关键性能指标(如带宽、失调电压)的范围是多少?最坏情况是怎样的?设计裕量:当前的设计距离性能失效的边界还有多远?是否足够安全?敏感性分析:电路的性能对哪些元器件的参数变化最敏感?蒙特卡洛仿真如何工作?其工作流程可以概括为以下几个步骤:建立模型:这是基础。晶圆厂会提供包含工艺偏差信息的PDK。PDK中的器件模型(如BSIM模型)不仅包含典型值,还包含了每个参数的标准差(σ)和分布类型(通常是高斯分布/正态分布)。例如,一个电阻的标称值是1kΩ,其标准差可能是50Ω。设置仿真:工程师在仿真工具(如Cadence Spectre, Synopsys HSPICE等)中设置一个普通的电路性能测试(如直流工作点、瞬态分析、交流分析)。定义运行次数:工程师指定蒙特卡洛仿真的次数,例如500次或1000次。次数越多,统计结果越准确,但计算时间也越长。随机抽样与循环仿真:仿真器开始第一次循环。它根据PDK中的统计模型,为电路中的每一个元件随机生成一套参数值(例如,这次循环中某个NMOS的Vth比标称值高了0.5mV,另一个电阻的阻值低了1%)。用这套随机参数对整个电路进行一次完整的性能仿真,并记录结果(如增益=79.8dB)。重复上述过程,直到达到指定的运行次数。每一次循环都相当于“生产”并“测试”了一个新的电路样本。结果分析:仿真完成后,工具会生成所有性能指标的统计报告和图表,例如:直方图:直观显示性能(如增益)的分布情况。理想情况下,它应该是一个集中在设计目标附近的正态分布曲线。统计摘要:给出平均值(mean)、标准差(sigma)、最小值(min)、最大值(max)以及指定西格玛水平(如3σ)下的数值。散点图:分析两个性能参数之间的相关性(例如,增益高的样本是否功耗也更大?)。一个简单的例子:差分对失调电压假设你设计了一个运算放大器的输入差分对。在理想情况下,两个完全相同的晶体管输入相同的电压,输出差应为零(失调电压Vos=0)。但在蒙特卡洛仿真中,仿真器会随机改变两个晶体管的阈值电压(Vth)、尺寸(W/L)等参数。每次仿真都会得到一个非零的失调电压。运行1000次后,你可能会发现:失调电压的平均值接近0。失调电压呈正态分布。99.7%的样本(3σ范围)的失调电压在±2mV以内。这样,你就可以非常有信心地对外宣称:“我的运放设计在3σ水平下的失调电压小于2mV”。总结方面 解释本质 一种基于随机抽样的统计分析方法。目的 评估工艺偏差对电路性能的影响,预测成品率和鲁棒性。输入 带有工艺偏差统计模型的电路网表和器件模型(来自PDK)。输出 电路性能的统计分布(直方图)、平均值、标准差、最坏情况值等。重要性 是现代模拟/混合信号芯片设计不可或缺的一环,是连接理想设计与现实制造的关键桥梁,确保设计能在大规模生产中保持高良率。因此,蒙特卡洛仿真是模拟电路设计师评估其设计在实际生产中是否“可靠”和“健壮”的最重要工具之一。 -

-
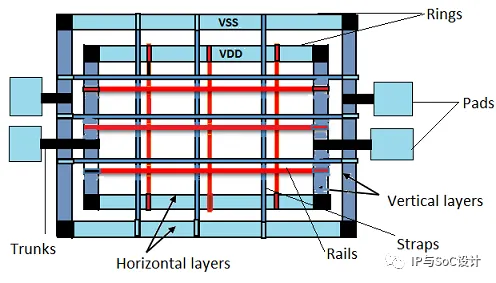
 博文速递:Power Plan 原创Feroz Ahmed IP与SoC设计2023年05月24日12:02江苏作者:Feroz Ahmed Choudhary PD Engineer(VLSI)Power Plan ·To connect Power to the Chip by considering issues like EM and IR Drop ·Power Routing also called Pre-Routing ·Pre-Routing includes creating Power Ring, Stripes/Mesh/Grid, and Standard Cell Power Rails ·Power Planning also includes Power Via insertion ·IO Rings are established through IO Cell abutment and through IO Filler Cells ·Power Trunks are constructed between Core Power Ring and Power Pads ·Technical information required for Power Planning: ·Total Dynamic Power info. will get from Compiler ·Technology File will provide Current Density (JMAX) ·LEF will prove the Metal Layer width ·Technology Library will provide Core VoltageLevels of Power DistributionRings ·VDD and VSS Rings are formed around the Core and MacroStripes ·Carries VDD and VSS around the chip ·Carries VDD and VSS from Rings across the chip ·Power Stripes are created in the Core Area to tap power from Core Rings to the core areaRails (Special Route) ·Connect VDD and VSS to the standard cell ·Standard Cell Rails are created to tap power from Power Stripes to Std. Cell Power/Ground PinsPower Vias ·Insert all Power Vias between Ring & Grid, Grid & Rail and Vertical Grid & Horizontal GridTrunks ·Connects Ring to Power PadCore Power ManagementVDD and VSS power rings are formed around the core and macro. In addition to this straps and trunks are created for macros as per the power requirement. Std cell rails are created to tap power from power straps to std cell power/ground pins.I/O Power ManagementPower rings are formed for I/O cells and trunks are constructed between core power ring and power pads.Power Planning Involves ·calculating number of power pins required ·Number of Rings, Stripes ·width of ring and stripes ·IR DropInputs of Power plan ·Netlist & SDC ·.lib , .lef & tech file ·Tlu+ file ·UPFIdeal Power distribution network has the following properties ·maintain a stable voltage with little noise ·Avoid wear out from EM and self heating ·Consume little chip area and wiring ·Easy to layoutPower Information ·The power information can obtain from the front end design. ·the synthesis tool reoprts static power information ·dynamic power can be calculated using value change dump (VCD) or switching activity interchange format (SAIF) file in conjunction with RTL description and test bench. ·Exhaustive test coverage is required for efficient calculation of peak power. this methodology is depicted in figure as shown below.PowerPlan : CalculationsUPF ContentsPower intent specifies ·Power Distribution Architecture: ·Power domains – Group of elements which share a common set of power supply requirements ·Supply rails – Power distribution (ports, nets, sets & switches) ·Shutdown control ·Power Strategy ·Power state tables – Legal combination of states of each power domain ·Operating voltages ·Usage of Special cells ·Isolation cells ·Level shifters ·Power switches ·Retention registersIsolation cells ·Powered off domains do not drive their outputs anymore and these outputs become floating nodes. This could be a problem when other active domains gets these floating nodes as input. It could result in crowbar current which affects the proper functioning of the powered up domain. ·Isolation cells (also called “clamps”) keep the turned off sub-block outputs at a predefined value. This is how the shut-down sub-block does not corrupt other active sub-block functionality. ·Isolation cells are powered by a constant supply and drive 0, 1 or latch the old value of the turned off domain. ·Isolation cells pass logic values during the normal mode of operation, but clamp it to some specified value when a control signal is asserted. ·Isolation cell clamps the output of powered down block to a specified value (‘0’, ‘1’, last) ·Gate type clamp cells (AND, OR) ·Transistor type clamp (pull-up, pull-down)Level Shifters ·Level shifters have the minimal functionality of a buffer. ·Necessary as most low-power designs have multi-voltage domains and/or employ dynamic voltage scaling. ·A level shifter swings a logic value in one voltage domain to the same logic value in another voltage domain. ·An ‘Up’ level shifter swings a logic value from a lower voltage domain to the same logic value in a higher voltage domain. ·A ‘Down’ level shifter swings a logic value from a higher voltage domain to the same logic value in a lower voltage domain.Internal circuit of level shifter.Retention Registers ·In order to reduce power consumption, memories are shut down where their power domain is switched off or when they are not in use. Registers are corrupted when power is switched off. Corruption is typically represented as ‘X’ (unknown). ·Some memories need to retain their values for fast wake-up. For these memories, only the memory array stays powered on during the shut-down while the peripheral interfaces are powered off. ·Retention registers keep their previous active value after being shut down. ·Retention registers save state information before a power domain is switched off and restore it when the power is turned back on. ·Retention registers comprise of two circuits. ·Standard register logic, supplied by primary power VDD ·Shadow latch retention circuitry, with alternate supply VDDB ·SAVE – transfers FF content into shadow latch during shutdown ·RESTORE – transfers state from shadow latch to FF when powered back onPower Switches ·Power switches are required to Gate the power supply of gated domain when not required. power switches are MT-CMOS (Multi Threshold) cells, which will have very high threshold voltage when device is OFF & very low threshold voltage when deviceis ON. ·power switches are inserted in power mesh & supply to all gated domain cells will be through power switches. hence a single/few switches are not enough. A strong network of power switchs connected in daisy chain fashion will be inserted in the design.There are 2 types of power switches header and footerHeader ·The header switch is implemented by PMOS transistors to control Vdd supply. ·PMOS transistor is less leaky than NMOS transistor of a same size. Header switches turn off VDD and keep VSS on. As the result, it allows a simple design of a pull-down transistor to isolate power-off cells and clamp output signals ·The disadvantage of the header switch is that PMOS has lower drive current than NMOS of a same size, though difference is reduced by strained silicon technology. As a result, a header switch implementation usually consumes more area than a footer switch implementation.Footer ·The footer switch is implemented by NMOS transistor to control VSS supply. ·The advantage of footer switch is the high drive and hence smaller area. ·However, NMOS is leakier than PMOS and a Designs become more sensitive to ground noiseFrequently Used Power Reduction TechniquesPower Gating: ·In a processor chip, certain areas of the chip will be idle and will be activated only for certain operations. But these areas are still provided with power for biasing. ·The power gating limits this unnecessary power being wasted by shuting down power for that area and resuming whenever needed. ·It is used for reducing LEAKAGE POWER or power consumption by switching off power supply to the non operational power domain of the chip during certain mode of operation. ·Header & footer switches, isolation cells, state retention flip flops are used for implementing power gating.Clock Gating: ·Clock gating limits the clock from being given to every register or flops in the processor. It disables the clock of an unused device. In clock gating the gated areas will still be provided with bias power. ·It is used for reducing DYNAMIC POWER by controlling switching activities on the clock path. ·Generally gate or latch or flip flop based block gating cells are used for implementing clock gating. ·50% of dynamic power is due to clock buffer. Since clock has highest toggle rate and often have higher drive strength to minimize clock delay. And the flops receive clocks dissipates some dynamic power even if input and output remains the same. Also clock buffer tree consumes power. One of the techniques to lower the dynamic power is clock gating. ·In load enabled flops, the output of the flops switches only when the enable is on. But clock switches continuously, increasing the dynamic power consumption. ·By converting load enable circuits to clock gating circuit dynamic power can be reduced. Normal clock gating circuit consists of an AND gate in the clock path with one input as enable. But when enable becomes one in between positive level of the clock a glitch is obtained. ·To remove the glitches due to AND gate, integrated clock gate is used. It has a negative triggered latch and an AND gate. ·Clock gating makes design more complex. Timing and CG timing closure becomes complex. Clock gating adds more gates to the design. Hence min bit width (minimum register bit width to be clock gated) should be wisely chosen, because the overall dynamic power consumption may increase.Voltage and Frequency Scaling: ·It changes the voltage and clock frequency to match the performance requirements for a given operation so as to minimize leakage. ·Different blocks are operated at variable supply voltages. The block voltage is dynamically adjusted based on performance requirements. ·Frequency of the block is dynamically adjusted. Works alongside with voltage scaling. Substrate Biasing: ·It changes the threshold voltage to reduce leakage current at the expense of slower switching times.Multiple Threshold Voltages: ·Uses different Vt in the circuit to reduce leakage but still satisfy timing constraints.Multiple Supply Voltages: ·Using Multi VDD reduces power consumption by powering down the not used voltage domain. Different blocks are operated at different supply voltages. Signals that cross voltage domain boundaries have to be level shifted.Memory Partitioning: ·The memory is split into several partitions. Not used ones can be powered down.Types of Power Dissipation:The power dissipation is classified in two categories: ·Static power dissipation ·Dynamic power dissipationStatic Power Dissipation:In this class, power will be dissipated irrespective of frequency and switching of the system. It is continuous and has become more dominant at lower node technologies. The structure and size of the device results in various leakage currents.Few reasons for static power dissipation are: ·Sub-threshold current ·Gate oxide leakage ·Diode reverse bias current ·Gate induced leakageIts hard to find the accurate amount of leakage currents but it mainly depends on supply voltage (VDD), threshold voltage (Vth), transistor size (W/L) and the doping concentration.Dynamic Power Dissipation:There are two reasons of dynamic power dissipation; Switching of the device and short circuit path from supply (VDD) to ground (VSS). This occurs during operation of the device. Signals change their logic state charging and discharging of output mode capacitor.Short-circuit Power Dissipation:Because of slower input transition, there will be certain duration of time “t”, for which both the devices (PMOS and NMOS) are turned ON. Now, there is a short circuit path from VDD to VSS. This short circuit power is given by:where, Vdd – Supply voltage, Isc – Short-circuit current and t – Short-circuit time. Short-circuit power is directly proportional to rise time and fall time.Switching Power Dissipation:Energy is drawn from the power supply to charge up the output mode capacitance. Charging up of the output cap causes transition from 0V to VDD. So, the power dissipated during charging and discharging of total load [output capacitance + net capacitance + input capacitance of driven cell(s)] is called Switching power dissipation. The switching power is given by:where, α – Switching activity factor, f – Operating frequency, VDD – Supply voltage & Cload – Load capacitance.Fundamental sources of power supply noise are IR Drop & Ldi/dt noise.IR Dropthe power supply in the chip is distributed uniformly through metal layers across the design and these metal layers have their finite amount of resistance. when we applied the volatge the current starts flowing through these metal layers and some voltage is dropped due to that resistance of a metal wire and current. this drop is called IR Drop. Because of IR drop, delay will increase and it violates the timing and this will increase noise and performance will be degraded.There are 2 types of IR Drop. ·Static IR Drop: This drop is independent of cell switching and this is calculated with the help of metal own resistance. ·Dynamic IR Drop: This drop is calculated with the help of the switching of cells. when a cell is switching at the active edge of the clock the cell requires large current or voltage to turn on but due to voltage drop suffficient amount of voltage is not reached to thr particular cell and cell may be goes into metastable state and effect the timing and performance.Methods to improve static IR Drop ·We can go for higher layers if available. ·Increase the width of the straps. ·Increase the number of wires. ·Check if any via is missing then add more via.Methods to improve Dynamic IR Drop ·Use De-Cap Cells. ·Increase the number of straps.Tools Used for IR Drop Analysis ·Redhawk from Apache ·Volatage storm from cadenceElectromigrationWhen a high density of current is flowing through metal layers, the atoms (electron) in the metal layers are displaced from their origional position causing open and shorts in the metal layers. Heating also accelerates EM because higher temperature cause a high number of metal ions to diffuseIn higher technology nodes we saw the EM on power and clock metal layers but now in lower nodes the signal metal layers are also needed to be analyzes due to an increased amount of current density.clock nets are more prone to EM because they have high switching activity because of this only we are avoiding to use high drive strength clock buffers to build the clock tree.Methods to solve EMIncrease the width of wireBuffer insertionDownsize the driverSwitch the net to higher metal layersAdding more vias来自微信
博文速递:Power Plan 原创Feroz Ahmed IP与SoC设计2023年05月24日12:02江苏作者:Feroz Ahmed Choudhary PD Engineer(VLSI)Power Plan ·To connect Power to the Chip by considering issues like EM and IR Drop ·Power Routing also called Pre-Routing ·Pre-Routing includes creating Power Ring, Stripes/Mesh/Grid, and Standard Cell Power Rails ·Power Planning also includes Power Via insertion ·IO Rings are established through IO Cell abutment and through IO Filler Cells ·Power Trunks are constructed between Core Power Ring and Power Pads ·Technical information required for Power Planning: ·Total Dynamic Power info. will get from Compiler ·Technology File will provide Current Density (JMAX) ·LEF will prove the Metal Layer width ·Technology Library will provide Core VoltageLevels of Power DistributionRings ·VDD and VSS Rings are formed around the Core and MacroStripes ·Carries VDD and VSS around the chip ·Carries VDD and VSS from Rings across the chip ·Power Stripes are created in the Core Area to tap power from Core Rings to the core areaRails (Special Route) ·Connect VDD and VSS to the standard cell ·Standard Cell Rails are created to tap power from Power Stripes to Std. Cell Power/Ground PinsPower Vias ·Insert all Power Vias between Ring & Grid, Grid & Rail and Vertical Grid & Horizontal GridTrunks ·Connects Ring to Power PadCore Power ManagementVDD and VSS power rings are formed around the core and macro. In addition to this straps and trunks are created for macros as per the power requirement. Std cell rails are created to tap power from power straps to std cell power/ground pins.I/O Power ManagementPower rings are formed for I/O cells and trunks are constructed between core power ring and power pads.Power Planning Involves ·calculating number of power pins required ·Number of Rings, Stripes ·width of ring and stripes ·IR DropInputs of Power plan ·Netlist & SDC ·.lib , .lef & tech file ·Tlu+ file ·UPFIdeal Power distribution network has the following properties ·maintain a stable voltage with little noise ·Avoid wear out from EM and self heating ·Consume little chip area and wiring ·Easy to layoutPower Information ·The power information can obtain from the front end design. ·the synthesis tool reoprts static power information ·dynamic power can be calculated using value change dump (VCD) or switching activity interchange format (SAIF) file in conjunction with RTL description and test bench. ·Exhaustive test coverage is required for efficient calculation of peak power. this methodology is depicted in figure as shown below.PowerPlan : CalculationsUPF ContentsPower intent specifies ·Power Distribution Architecture: ·Power domains – Group of elements which share a common set of power supply requirements ·Supply rails – Power distribution (ports, nets, sets & switches) ·Shutdown control ·Power Strategy ·Power state tables – Legal combination of states of each power domain ·Operating voltages ·Usage of Special cells ·Isolation cells ·Level shifters ·Power switches ·Retention registersIsolation cells ·Powered off domains do not drive their outputs anymore and these outputs become floating nodes. This could be a problem when other active domains gets these floating nodes as input. It could result in crowbar current which affects the proper functioning of the powered up domain. ·Isolation cells (also called “clamps”) keep the turned off sub-block outputs at a predefined value. This is how the shut-down sub-block does not corrupt other active sub-block functionality. ·Isolation cells are powered by a constant supply and drive 0, 1 or latch the old value of the turned off domain. ·Isolation cells pass logic values during the normal mode of operation, but clamp it to some specified value when a control signal is asserted. ·Isolation cell clamps the output of powered down block to a specified value (‘0’, ‘1’, last) ·Gate type clamp cells (AND, OR) ·Transistor type clamp (pull-up, pull-down)Level Shifters ·Level shifters have the minimal functionality of a buffer. ·Necessary as most low-power designs have multi-voltage domains and/or employ dynamic voltage scaling. ·A level shifter swings a logic value in one voltage domain to the same logic value in another voltage domain. ·An ‘Up’ level shifter swings a logic value from a lower voltage domain to the same logic value in a higher voltage domain. ·A ‘Down’ level shifter swings a logic value from a higher voltage domain to the same logic value in a lower voltage domain.Internal circuit of level shifter.Retention Registers ·In order to reduce power consumption, memories are shut down where their power domain is switched off or when they are not in use. Registers are corrupted when power is switched off. Corruption is typically represented as ‘X’ (unknown). ·Some memories need to retain their values for fast wake-up. For these memories, only the memory array stays powered on during the shut-down while the peripheral interfaces are powered off. ·Retention registers keep their previous active value after being shut down. ·Retention registers save state information before a power domain is switched off and restore it when the power is turned back on. ·Retention registers comprise of two circuits. ·Standard register logic, supplied by primary power VDD ·Shadow latch retention circuitry, with alternate supply VDDB ·SAVE – transfers FF content into shadow latch during shutdown ·RESTORE – transfers state from shadow latch to FF when powered back onPower Switches ·Power switches are required to Gate the power supply of gated domain when not required. power switches are MT-CMOS (Multi Threshold) cells, which will have very high threshold voltage when device is OFF & very low threshold voltage when deviceis ON. ·power switches are inserted in power mesh & supply to all gated domain cells will be through power switches. hence a single/few switches are not enough. A strong network of power switchs connected in daisy chain fashion will be inserted in the design.There are 2 types of power switches header and footerHeader ·The header switch is implemented by PMOS transistors to control Vdd supply. ·PMOS transistor is less leaky than NMOS transistor of a same size. Header switches turn off VDD and keep VSS on. As the result, it allows a simple design of a pull-down transistor to isolate power-off cells and clamp output signals ·The disadvantage of the header switch is that PMOS has lower drive current than NMOS of a same size, though difference is reduced by strained silicon technology. As a result, a header switch implementation usually consumes more area than a footer switch implementation.Footer ·The footer switch is implemented by NMOS transistor to control VSS supply. ·The advantage of footer switch is the high drive and hence smaller area. ·However, NMOS is leakier than PMOS and a Designs become more sensitive to ground noiseFrequently Used Power Reduction TechniquesPower Gating: ·In a processor chip, certain areas of the chip will be idle and will be activated only for certain operations. But these areas are still provided with power for biasing. ·The power gating limits this unnecessary power being wasted by shuting down power for that area and resuming whenever needed. ·It is used for reducing LEAKAGE POWER or power consumption by switching off power supply to the non operational power domain of the chip during certain mode of operation. ·Header & footer switches, isolation cells, state retention flip flops are used for implementing power gating.Clock Gating: ·Clock gating limits the clock from being given to every register or flops in the processor. It disables the clock of an unused device. In clock gating the gated areas will still be provided with bias power. ·It is used for reducing DYNAMIC POWER by controlling switching activities on the clock path. ·Generally gate or latch or flip flop based block gating cells are used for implementing clock gating. ·50% of dynamic power is due to clock buffer. Since clock has highest toggle rate and often have higher drive strength to minimize clock delay. And the flops receive clocks dissipates some dynamic power even if input and output remains the same. Also clock buffer tree consumes power. One of the techniques to lower the dynamic power is clock gating. ·In load enabled flops, the output of the flops switches only when the enable is on. But clock switches continuously, increasing the dynamic power consumption. ·By converting load enable circuits to clock gating circuit dynamic power can be reduced. Normal clock gating circuit consists of an AND gate in the clock path with one input as enable. But when enable becomes one in between positive level of the clock a glitch is obtained. ·To remove the glitches due to AND gate, integrated clock gate is used. It has a negative triggered latch and an AND gate. ·Clock gating makes design more complex. Timing and CG timing closure becomes complex. Clock gating adds more gates to the design. Hence min bit width (minimum register bit width to be clock gated) should be wisely chosen, because the overall dynamic power consumption may increase.Voltage and Frequency Scaling: ·It changes the voltage and clock frequency to match the performance requirements for a given operation so as to minimize leakage. ·Different blocks are operated at variable supply voltages. The block voltage is dynamically adjusted based on performance requirements. ·Frequency of the block is dynamically adjusted. Works alongside with voltage scaling. Substrate Biasing: ·It changes the threshold voltage to reduce leakage current at the expense of slower switching times.Multiple Threshold Voltages: ·Uses different Vt in the circuit to reduce leakage but still satisfy timing constraints.Multiple Supply Voltages: ·Using Multi VDD reduces power consumption by powering down the not used voltage domain. Different blocks are operated at different supply voltages. Signals that cross voltage domain boundaries have to be level shifted.Memory Partitioning: ·The memory is split into several partitions. Not used ones can be powered down.Types of Power Dissipation:The power dissipation is classified in two categories: ·Static power dissipation ·Dynamic power dissipationStatic Power Dissipation:In this class, power will be dissipated irrespective of frequency and switching of the system. It is continuous and has become more dominant at lower node technologies. The structure and size of the device results in various leakage currents.Few reasons for static power dissipation are: ·Sub-threshold current ·Gate oxide leakage ·Diode reverse bias current ·Gate induced leakageIts hard to find the accurate amount of leakage currents but it mainly depends on supply voltage (VDD), threshold voltage (Vth), transistor size (W/L) and the doping concentration.Dynamic Power Dissipation:There are two reasons of dynamic power dissipation; Switching of the device and short circuit path from supply (VDD) to ground (VSS). This occurs during operation of the device. Signals change their logic state charging and discharging of output mode capacitor.Short-circuit Power Dissipation:Because of slower input transition, there will be certain duration of time “t”, for which both the devices (PMOS and NMOS) are turned ON. Now, there is a short circuit path from VDD to VSS. This short circuit power is given by:where, Vdd – Supply voltage, Isc – Short-circuit current and t – Short-circuit time. Short-circuit power is directly proportional to rise time and fall time.Switching Power Dissipation:Energy is drawn from the power supply to charge up the output mode capacitance. Charging up of the output cap causes transition from 0V to VDD. So, the power dissipated during charging and discharging of total load [output capacitance + net capacitance + input capacitance of driven cell(s)] is called Switching power dissipation. The switching power is given by:where, α – Switching activity factor, f – Operating frequency, VDD – Supply voltage & Cload – Load capacitance.Fundamental sources of power supply noise are IR Drop & Ldi/dt noise.IR Dropthe power supply in the chip is distributed uniformly through metal layers across the design and these metal layers have their finite amount of resistance. when we applied the volatge the current starts flowing through these metal layers and some voltage is dropped due to that resistance of a metal wire and current. this drop is called IR Drop. Because of IR drop, delay will increase and it violates the timing and this will increase noise and performance will be degraded.There are 2 types of IR Drop. ·Static IR Drop: This drop is independent of cell switching and this is calculated with the help of metal own resistance. ·Dynamic IR Drop: This drop is calculated with the help of the switching of cells. when a cell is switching at the active edge of the clock the cell requires large current or voltage to turn on but due to voltage drop suffficient amount of voltage is not reached to thr particular cell and cell may be goes into metastable state and effect the timing and performance.Methods to improve static IR Drop ·We can go for higher layers if available. ·Increase the width of the straps. ·Increase the number of wires. ·Check if any via is missing then add more via.Methods to improve Dynamic IR Drop ·Use De-Cap Cells. ·Increase the number of straps.Tools Used for IR Drop Analysis ·Redhawk from Apache ·Volatage storm from cadenceElectromigrationWhen a high density of current is flowing through metal layers, the atoms (electron) in the metal layers are displaced from their origional position causing open and shorts in the metal layers. Heating also accelerates EM because higher temperature cause a high number of metal ions to diffuseIn higher technology nodes we saw the EM on power and clock metal layers but now in lower nodes the signal metal layers are also needed to be analyzes due to an increased amount of current density.clock nets are more prone to EM because they have high switching activity because of this only we are avoiding to use high drive strength clock buffers to build the clock tree.Methods to solve EMIncrease the width of wireBuffer insertionDownsize the driverSwitch the net to higher metal layersAdding more vias来自微信 -
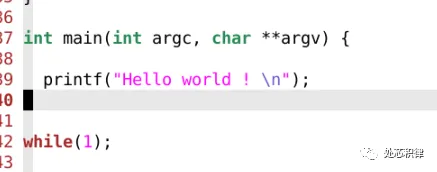
 SOC验证C代码中如何打印字符串? 嵌入式微处理器2023年04月27日13:00四川学过C语言都知道,在程序中添加打印信息有助于我们追踪程序执行的情况。特别是debug的时候,打印一些log信息对快速定位到问题非常有帮助。怎么在SOC验证的C代码中打印字符串呢?用printf ?下面,我们来试一下:执行结果:没有出现 Hello world。这种结果是符合预期的。C code 通过GCC编译生成bin文件然后送到CPU中按指令进行执行。我们看下这段代码编译出来的指令是什么?这里 printf 编译出来是jump到一个puts的函数里面。puts函数又是什么呢?puts 又跳到 _puts_r ,依次下去,由printf 编译出了一系列的指令代码。由于CPU最终综合成版图,因此在CPU的RTL代码中不会存在读到某条指令打印一个字符串的功能。所以单纯的调用printf 并不会在log中打印字符串信息。如何实现打印?两个思路,第一个思路,在SOC的TB里面增加一个CPU bus的monitor,我们在monitor中实现一个功能,当看到特定地址,特定数据的时候,开始收集要打印的字符串,当看到特定地址,另外一个特定数据的时候,结束字符串的收集,并将收集到字符串打印。以下是我们在一个project中看到特殊数据 24’hdddd_11xx 开始收集字符串。以下是我们在一个project中看到特殊数据 24’hdddd_eeee 时打印字符串。这样,我们可以在c里面实现一个打印字符串的函数。通过上面这种手段,我们巧妙的将C语言的打印和 verilog的 $display 打印连接起来。我们来看看效果Hello World 打印出来了。我们再看看 puts编译后的代码是什么?这次 puts并没有跳转到 _puts_r ,而是向特定地址发送特定数据表示开始,然后传输字符串,并以特定数据结束。当我们的monitor检查到这些特殊的数据时就会打印出log信息。上面打印的方式可以解决在SOC验证环境中打印 字符串的问题,但是在芯片流片回来之后,在C中调用上述函数还能打印吗?显然是不可以的,因为这个时候外部的monitor都没有了,更别说不能综合的display函数等。下面介绍一种更加普遍的使用方法。我们在嵌入式硬件开发的过程中经常用到串口调试工具。通过简单的几根线与电脑连接,然后用串口调试助手就能将SOC和电脑调试界面连接起来。因此,在我们SOC验证环境中集成UART的slave device,在UART device收到数据后,打印出字符串信息是一个很好的选择。为此,我们通过向uart device写字符串的形式,然后在UART device中实现打印功能。我们来测试下用上面这种方式打印的效果,prints 是我们向uart 发送字符串的函数。下面是执行效果:同样实现了打印,而且这种打印方式在后续芯片流片回来之后可以通过串口调试 查看打印的信息。看到这里,大家明白怎么在SOC中实现字符串打印了吧~
SOC验证C代码中如何打印字符串? 嵌入式微处理器2023年04月27日13:00四川学过C语言都知道,在程序中添加打印信息有助于我们追踪程序执行的情况。特别是debug的时候,打印一些log信息对快速定位到问题非常有帮助。怎么在SOC验证的C代码中打印字符串呢?用printf ?下面,我们来试一下:执行结果:没有出现 Hello world。这种结果是符合预期的。C code 通过GCC编译生成bin文件然后送到CPU中按指令进行执行。我们看下这段代码编译出来的指令是什么?这里 printf 编译出来是jump到一个puts的函数里面。puts函数又是什么呢?puts 又跳到 _puts_r ,依次下去,由printf 编译出了一系列的指令代码。由于CPU最终综合成版图,因此在CPU的RTL代码中不会存在读到某条指令打印一个字符串的功能。所以单纯的调用printf 并不会在log中打印字符串信息。如何实现打印?两个思路,第一个思路,在SOC的TB里面增加一个CPU bus的monitor,我们在monitor中实现一个功能,当看到特定地址,特定数据的时候,开始收集要打印的字符串,当看到特定地址,另外一个特定数据的时候,结束字符串的收集,并将收集到字符串打印。以下是我们在一个project中看到特殊数据 24’hdddd_11xx 开始收集字符串。以下是我们在一个project中看到特殊数据 24’hdddd_eeee 时打印字符串。这样,我们可以在c里面实现一个打印字符串的函数。通过上面这种手段,我们巧妙的将C语言的打印和 verilog的 $display 打印连接起来。我们来看看效果Hello World 打印出来了。我们再看看 puts编译后的代码是什么?这次 puts并没有跳转到 _puts_r ,而是向特定地址发送特定数据表示开始,然后传输字符串,并以特定数据结束。当我们的monitor检查到这些特殊的数据时就会打印出log信息。上面打印的方式可以解决在SOC验证环境中打印 字符串的问题,但是在芯片流片回来之后,在C中调用上述函数还能打印吗?显然是不可以的,因为这个时候外部的monitor都没有了,更别说不能综合的display函数等。下面介绍一种更加普遍的使用方法。我们在嵌入式硬件开发的过程中经常用到串口调试工具。通过简单的几根线与电脑连接,然后用串口调试助手就能将SOC和电脑调试界面连接起来。因此,在我们SOC验证环境中集成UART的slave device,在UART device收到数据后,打印出字符串信息是一个很好的选择。为此,我们通过向uart device写字符串的形式,然后在UART device中实现打印功能。我们来测试下用上面这种方式打印的效果,prints 是我们向uart 发送字符串的函数。下面是执行效果:同样实现了打印,而且这种打印方式在后续芯片流片回来之后可以通过串口调试 查看打印的信息。看到这里,大家明白怎么在SOC中实现字符串打印了吧~ -
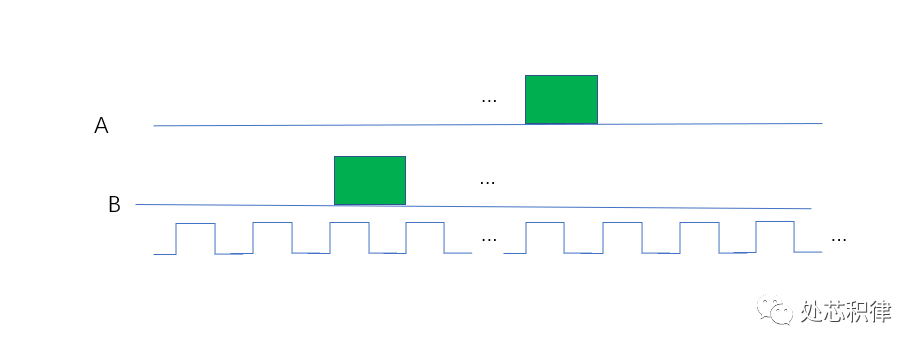
 芯片验证随机(random)的六宗罪 IP与SoC设计2023年04月19日12:04江苏以前看到不少验证技术书籍都在说验证环境中随机怎么怎么好,然后为了随机,UVM,SV 提供了什么什么支持。但是最近的一些工作小编发现在验证中采用随机存在很多缺点。下面小编带大家看看使用随机带来的六宗罪。第一宗罪:难以debug出现fail的test,当debug完,对设计和验证环境做了改动,可能无法复现fail的场景。如何确保发现的testbench的问题,或者RTL的问题有真的修掉?一般的做法是用同样的seed,然后跑一遍之前的fail的test。但是有很多时候,由于环境的文件,约束等改变,再用同样的seed 跑fail 的test 和之前的行为不一致,从而错误的认为问题已经修掉。第二宗罪:难以覆盖到特定场景有些场景通过随机撞到的概率非常低。如下图所示,C = A &&B,在下图场景中想通过 随机到 (A==1)&&(B==1)的 场景,非常难。第三宗罪:验证时间不确定回归结果不可靠。一次通过率100%,不代表次次回归100%。一次回归可能100%,第二次回归又变成90%。连续10次回归100%,第十一次回归又出现fail的test。第四宗罪:重复测试用例很多浪费太多license 和服务器资源。因为单次regression不能保证没有问题,所以要周周跑,月月跑,一直跑到tapout,这浪费了很多license和服务器资源。特别是有些test 打到的场景重复,做一些无效验证,给公司资源造成极大浪费。第五宗罪:覆盖率收集耗费资源coverage 收敛比较耗时间和资源。由于随机约束造成不同场景出现的概率不一样,通过随机测试将代码覆盖率和功能覆盖率补全需要经过大量的回归测试。coverage的收敛速度没有直接测试来得快。下面是一个案例,在跑完一版regression后,功能覆盖率是80.49%。我们想将该功能覆盖率补全,采用直接测试用例,我们调用了5次测试,可以将覆盖率打到95.90% ,剩下的部分可以waive掉。当我们采用随机测试,调用了5次随机测试,覆盖率为90.62%。当我们采用随机测试,调用了10次随机测试,覆盖率为93.97%。当我们采用随机测试,调用了20次随机测试,覆盖率为95.90%,达到了和直接测试同样的效果。第六宗罪:场景打不全随机验证打不全所有场景如上图所示,随机的行为很难将所有的测试路径都打到。随机有没有好处呢?当然有,比如探索更多的场景:随机验证可以探索更多的测试场景,覆盖更多的状态空间。这可以帮助发现设计中的潜在问题和漏洞,从而提高验证的质量。发现意外错误:随机测试可以揭示一些设计者未曾考虑的异常情况,以及在正常测试中可能被忽略的边缘情况。这有助于找到并修复一些潜在的设计错误。减少人为偏见:手动创建测试用例可能受到验证工程师的认知偏见和经验限制的影响。随机验证方法可以降低这种偏见对验证结果的影响,从而提高验证的可靠性。减少人工编写测试用例的时间和精力:随机验证方法可以自动生成大量测试用例,从而减少人工编写测试用例的时间和精力。这有助于缩短验证周期,提高验证效率。更好地应对复杂性:随着芯片设计变得越来越复杂,人工创建足够多的测试用例以覆盖所有可能的场景变得越来越困难。随机验证方法可以在面对复杂设计时自动生成更多的测试用例,从而更好地应对这种复杂性。使用随机验证存在很多问题,但它仍然是一种非常有效的验证方法。为了克服这些缺点,我们可以将随机验证与其他验证方法(如指导性验证、形式验证等)相结合,以实现更全面、有效的芯片验证。来自微信
芯片验证随机(random)的六宗罪 IP与SoC设计2023年04月19日12:04江苏以前看到不少验证技术书籍都在说验证环境中随机怎么怎么好,然后为了随机,UVM,SV 提供了什么什么支持。但是最近的一些工作小编发现在验证中采用随机存在很多缺点。下面小编带大家看看使用随机带来的六宗罪。第一宗罪:难以debug出现fail的test,当debug完,对设计和验证环境做了改动,可能无法复现fail的场景。如何确保发现的testbench的问题,或者RTL的问题有真的修掉?一般的做法是用同样的seed,然后跑一遍之前的fail的test。但是有很多时候,由于环境的文件,约束等改变,再用同样的seed 跑fail 的test 和之前的行为不一致,从而错误的认为问题已经修掉。第二宗罪:难以覆盖到特定场景有些场景通过随机撞到的概率非常低。如下图所示,C = A &&B,在下图场景中想通过 随机到 (A==1)&&(B==1)的 场景,非常难。第三宗罪:验证时间不确定回归结果不可靠。一次通过率100%,不代表次次回归100%。一次回归可能100%,第二次回归又变成90%。连续10次回归100%,第十一次回归又出现fail的test。第四宗罪:重复测试用例很多浪费太多license 和服务器资源。因为单次regression不能保证没有问题,所以要周周跑,月月跑,一直跑到tapout,这浪费了很多license和服务器资源。特别是有些test 打到的场景重复,做一些无效验证,给公司资源造成极大浪费。第五宗罪:覆盖率收集耗费资源coverage 收敛比较耗时间和资源。由于随机约束造成不同场景出现的概率不一样,通过随机测试将代码覆盖率和功能覆盖率补全需要经过大量的回归测试。coverage的收敛速度没有直接测试来得快。下面是一个案例,在跑完一版regression后,功能覆盖率是80.49%。我们想将该功能覆盖率补全,采用直接测试用例,我们调用了5次测试,可以将覆盖率打到95.90% ,剩下的部分可以waive掉。当我们采用随机测试,调用了5次随机测试,覆盖率为90.62%。当我们采用随机测试,调用了10次随机测试,覆盖率为93.97%。当我们采用随机测试,调用了20次随机测试,覆盖率为95.90%,达到了和直接测试同样的效果。第六宗罪:场景打不全随机验证打不全所有场景如上图所示,随机的行为很难将所有的测试路径都打到。随机有没有好处呢?当然有,比如探索更多的场景:随机验证可以探索更多的测试场景,覆盖更多的状态空间。这可以帮助发现设计中的潜在问题和漏洞,从而提高验证的质量。发现意外错误:随机测试可以揭示一些设计者未曾考虑的异常情况,以及在正常测试中可能被忽略的边缘情况。这有助于找到并修复一些潜在的设计错误。减少人为偏见:手动创建测试用例可能受到验证工程师的认知偏见和经验限制的影响。随机验证方法可以降低这种偏见对验证结果的影响,从而提高验证的可靠性。减少人工编写测试用例的时间和精力:随机验证方法可以自动生成大量测试用例,从而减少人工编写测试用例的时间和精力。这有助于缩短验证周期,提高验证效率。更好地应对复杂性:随着芯片设计变得越来越复杂,人工创建足够多的测试用例以覆盖所有可能的场景变得越来越困难。随机验证方法可以在面对复杂设计时自动生成更多的测试用例,从而更好地应对这种复杂性。使用随机验证存在很多问题,但它仍然是一种非常有效的验证方法。为了克服这些缺点,我们可以将随机验证与其他验证方法(如指导性验证、形式验证等)相结合,以实现更全面、有效的芯片验证。来自微信